Os¶
文档信息(Document Information)¶
版本历史(Version History)¶
日期(Date) |
作者(Author) |
版本(Version) |
状态(Status) |
说明(Description) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
2025/01/13 |
Chao.Ye |
V0.1 |
发布(Release) |
首次发布(First release) |
2025/04/04 |
Chao.Ye |
V1.0 |
发布(Release) |
正式发布(Official release) |
参考文档(References)¶
编号(Number) |
分类(Classification) |
标题(Title) |
版本(Version) |
|---|---|---|---|
[1] |
Autosar |
AUTOSAR_SWS_OS.pdf |
R23-11 |
[2] |
ISO |
ISO 17356-3:2005 Part 3:OSEK/VDX Operating System(OS).pdf |
V2.2.3 |
术语与简写(Terms and Abbreviations)¶
术语(Terms)¶
术语(Term) |
解释(Explanation) |
|---|---|
OSEK/VDX |
汽车电子类开放系统和对应接口标准/汽车分布式执行标准(Open Systems and Corresponding Interfaces for Automotive Electronics / Vehicle Distributed Execution standard) |
Scalability Class(可扩展类别) |
本文档介绍的ORIENTAIS OS功能(例如内存保护或时间保护)可以组合在一起,以根据应用程序的需要自定义操作系统。有4个定义的功能组,称为可扩展类别(SC1/SC2/SC3/SC4)。(The ORIENTAIS OS functions (such as memory protection or time protection) introduced in this document can be combined to customize the operating system according to the needs of the application. There are 4 defined function groups called Scalability Classes (SC1/SC2/SC3/SC4).) |
OS-Application(操作系统对象集) |
操作系统对象的集合(A collection of operating system objects) 可信:可以在特权模式下执行并且可以不受限制地访问API和硬件资源的OS-Application。只有受信任的OS-Application才能提供受信任的功能。(Trusted: An OS-Application that can execute in privileged mode and has unrestricted access to APIs and hardware resources. Only trusted OS-Applications can provide trusted functions.) 不可信:在非特权模式下执行的OS-Application已限制对API和硬件资源的访问。(Untrusted: An OS-Application that executes in unprivileged mode with restricted access to APIs and hardware resources.) |
Access Right(访问权限) |
OS-Application的对象(例如Task,ISR,hook函数)具有对内存,操作系统服务或对象集的访问或操作的许可权限。(Objects of an OS-Application (such as Task, ISR, hook function) have permission to access or operate on memory, operating system services, or object sets.) |
Expiry Point(溢出点) |
调度表上的偏移量,从零开始计算,ORIENTAIS OS将在该偏移量处激活任务和(或)设置事件。(An offset on the schedule table, calculated from zero, at which the ORIENTAIS OS will activate tasks and/or set events.) 初始溢出点:具有最小偏移量的溢出点。(Initial Expiry Point: The expiry point with the smallest offset.) 结束溢出点:具有最大偏移量的溢出点。(End Expiry Point: The expiry point with the largest offset.) |
Schedule Table(调度表) |
调度表是一组不同时间偏移溢出点的集合。(A schedule table is a collection of expiry points with different time offsets.) |
Spinlock(自旋锁) |
自旋锁是一种锁定机制,其中任务或中断在循环(“自旋”)中等待,反复检查共享变量是否变为某个值,该值表示自旋锁的当前锁定状态。在多核系统中,变量的比较和更改通常需要原子操作。由于任务或中断保持活动状态(等待其他核释放自旋锁),但没有执行任何有用的操作,因此自旋锁是一种忙等机制。(A spinlock is a locking mechanism where a task or interrupt waits in a loop (“spins”), repeatedly checking if a shared variable changes to a value indicating the current locked state of the spinlock. In multi-core systems, the comparison and modification of variables usually require atomic operations. Since the task or interrupt remains active (waiting for another core to release the spinlock) but does not perform any useful operations, a spinlock is a busy-wait mechanism.) |
Spinlock Variable(自旋锁变量) |
自旋锁变量是自旋锁使用的共享变量,用于表示自旋锁是空闲还是已被占用。(A spinlock variable is a shared variable used by a spinlock to indicate whether the spinlock is idle or occupied.) |
Trusted Function(可信函数) |
由受信任的OS-Application提供的服务(函数),可以由其他OS-Application(受信任或不受信任)使用(调用)。(A service (function) provided by a trusted OS-Application that can be used (called) by other OS-Applications (trusted or untrusted).) |
Master core(主核) |
主核是硬件启动后自动启动的核。(The master core is the core that starts automatically after the hardware is powered on.) |
Slave Core(从核) |
从核是由主核激活后启动的核。(The slave core is the core that starts after being activated by the master core.) |
简写(Abbreviations)¶
缩略词(Abbreviations) |
描述(Description) |
解释(Explanation) |
|---|---|---|
API |
Application Programming Interface (应用程序接口) |
A set of routines, protocols, and tools for building software applications (用于构建软件应用程序的一组例程、协议和工具) |
HW |
Hardware (硬件) |
A physical component of a computer system (计算机系统的物理组件) |
SW |
Software (软件) |
A set of programs and data that make up a computer system (组成计算机系统的一组程序和数据) |
ISR |
Interrupt Service Routine (中断服务程序) |
A program that runs in response to an interrupt (响应中断的程序) |
MCU |
Microcontroller Unit (微控制器单元) |
A small, general-purpose computer designed to control small electronic devices (由小而General-purpose计算机设计的小型通用计算机,用于控制小型电子设备) |
MPU |
Memory Protection Unit (存储器保护单元) |
A hardware component that provides memory protection services to the operating system (一个提供内存保护服务的硬件组件,用于操作系统) |
OS |
Operating System (操作系统) |
A computer operating system that provides services to other operating systems and applications (一个为其他操作系统和应用程序提供服务,并运行在计算机上的操作系统) |
STM |
System Timer (系统定时器) |
A peripheral component that provides a timer service to the operating system (一个提供定时服务的外设组件,用于操作系统) |
MISRA |
The Motor Industry Software Reliability Association (电机工业软件可靠性协会) |
A non-profit organization that promotes software reliability in the motor industry (一个非营利组织,用于电机行业推广软件可靠性) |
TCL |
Tool Confidence Level (工具置信度水平) |
A level of confidence in the quality of a software tool (软件工具的可信度水平) |
简介(Introduction)¶
Os是为汽车电子领域开发的可抢占,多任务,高性能,低资源消耗和可定制的实时操作系统。它符合AUTOSAR R19标准(汽车电子领域中广泛接受的标准),并满足MISRA-C 2012编程规范。
Os is a preemptive, multi-tasking, high-performance, low-resource-consuming, and customizable real-time operating system developed for the automotive electronics field. It complies with the AUTOSAR R19 standard (a widely accepted standard in the automotive electronics field) and meets the MISRA-C 2012 programming specifications.
ORIENTAIS OS满足以下要求:
ORIENTAIS OS meets the following requirements:
系统是完全静态配置的,在正常运行期间不允许进行任何配置更改;
The system is completely statically configured, and no configuration changes are allowed during normal operation;
系统易于移植;
The system is easy to port;
系统具有灵活的可扩展性。
The system has flexible scalability.
ORIENTAIS OS具有广泛的可扩展性,完善的系统服务,各种调度机制以及便捷的配置功能,可以适应各种需求并在多种硬件平台上有效地运行。
ORIENTAIS OS features extensive scalability, comprehensive system services, various scheduling mechanisms, and convenient configuration functions, enabling it to adapt to various requirements and operate efficiently on multiple hardware platforms.
用户须在ORIENTAIS配置工具OS上修改参数以生成所需的代码,并将生成的代码加入到集成项目中。
Users must modify parameters in the ORIENTAIS configuration tool OS to generate the required code and integrate the generated code into the project.
功能描述(Function Description)¶
特性(Features)¶
ORIENTAIS OS使用静态配置和动态管理将其功能集成到相关对象中。对象之间的相互调用是通过相关接口实现的。
ORIENTAIS OS integrates its functions into related objects using static configuration and dynamic management. Interactions between objects are implemented through corresponding interfaces.
ORIENTAIS OS软件结构见
The software structure of ORIENTAIS OS is shown in
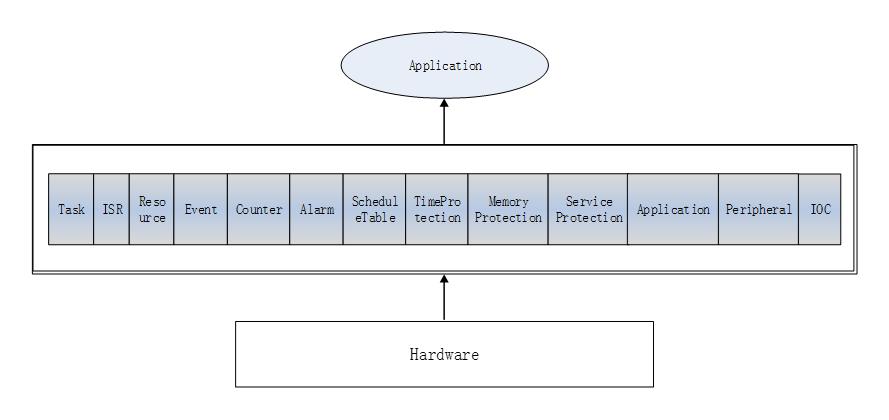
ORIENTAIS OS架构框图(ORIENTAIS OS Architecture Diagram)¶
各部分的功能如下:
The functions of each part are as follows:
Task management
它主要实现拓展任务和基本任务的激活,终止,重新调度,以及信息的获取。
It mainly implements the activation, termination, rescheduling of extended tasks and basic tasks, as well as information acquisition.
Interrupt management
它主要实现全局中断,ORIENTAIS OS中断的打开和关闭功能。
It mainly implements enabling and disabling of global interrupts and ORIENTAIS OS interrupts.
Resource management
ORIENTAIS OS中的资源是一种互斥访问资源的方法。资源管理主要实现资源的获取和释放等功能。
Resources in ORIENTAIS OS provide a method for mutually exclusive access to resources. Resource management mainly implements functions such as resource acquisition and release.
Event management
它是任务之间的同步机制,而不是独立的对象,必须依附于拓展任务。事件管理主要负责实现设置,等待,查询和清除事件功能。
It is a synchronization mechanism between tasks rather than an independent object, and must be attached to extended tasks. Event management is mainly responsible for implementing functions such as setting, waiting, querying, and clearing events.
Counter management
它主要实现计数器计数,信息查询等功能,并为Alarm提供定时计数功能。
It mainly implements functions such as counter counting and information querying, and provides timing counting functions for Alarm.
Alarm management
它主要实现计时功能,并在预定时间到达时触发相关操作,例如设置事件,激活任务和执行回调。
It mainly implements timing functions and triggers related operations when scheduled time is reached, such as setting events, activating tasks, and executing callbacks.
ScheduleTable management
它主要实现启动,停止和同步调度表的功能。
It mainly implements the functions of starting, stopping, and synchronizing schedule tables.
Timing protection management
为了安全和准确的时间保护,ORIENTAIS OS必须在运行时控制这些因素,以确保任务/ ISR能够满足各自的截止时间。该模块主要为任务/中断的各种截止时间实施操作系统的保护。
For safe and accurate time protection, ORIENTAIS OS must control these factors during runtime to ensure that tasks/ISRs can meet their respective deadlines. This module mainly implements operating system protection for various deadlines of tasks/interrupts.
Memory protection management
内存保护的最终目标是为空间中正在运行的实体(任务/中断)提供访问保护,即”空间隔离”。内存保护提供相应任务的内存访问。内存保护为2类中断提供内存分区和相应的段访问权限。Hook为内存保护提供ProtectionHook系统服务。
The ultimate goal of memory protection is to provide access protection for running entities (tasks/interrupts) in the space, namely “spatial isolation”. Memory protection provides memory access for corresponding tasks. It provides memory partitions and corresponding segment access permissions for Category 2 interrupts. Hook provides ProtectionHook system services for memory protection.
Service protection management
运行时,服务保护可以防止服务调用不会破坏ORIENTAIS OS本身。
During runtime, service protection prevents service calls from damaging ORIENTAIS OS itself.
Application management
有效资源的分配是通过OS-Application实现的。如果用户使用OS-Application,则所有任务,中断,资源,计数器,警报和调度表必须属于同一OS-Application。OS-Application分为可信和不可信两类。受信任的OS-Application在特权模式下运行,不受信任的OS-Application以用户模式运行。用户模式下的OS-Application无法直接访问内核资源。如果用户需要访问内核资源,则用户必须进入特权模式。当然,这里有一个前提,OS内核本身是受信任的。受信任的OS-Application可以提供外部服务,包括对不受信任的OS-Application的服务。
Effective resource allocation is achieved through OS-Applications. If OS-Applications are used, all tasks, interrupts, resources, counters, alarms, and schedule tables must belong to the same OS-Application. OS-Applications are categorized as trusted and untrusted. Trusted OS-Applications run in privileged mode, while untrusted OS-Applications run in user mode. OS-Applications in user mode cannot directly access kernel resources. To access kernel resources, users must enter privileged mode. This requires the OS kernel itself to be trusted. Trusted OS-Applications can provide external services, including services to untrusted OS-Applications.
Spinlock management
在多核系统中,一些资源涉及跨核互斥使用,因此需要引入自旋锁。在任何时候,最多只有一个执行单元获取该锁,其他执行单元不断循环以检查旋转锁的持有者是否已释放自旋锁。
In multi-core systems, spinlocks are introduced for resources requiring cross-core mutually exclusive access. At any time, only one execution unit can acquire the lock, while other units continuously check whether the spinlock holder has released it.
Peripheral management
外设访问功能主要用于在内存保护打开的情况下,不可信的 Application 去访问 MCU 的硬件寄存器。
The peripheral access function is mainly used to allow untrusted Applications to access MCU hardware registers when memory protection is enabled.
IOC management
IOC 为OS提供的通信机制,能够实现跨核、跨任务、跨分区(OS-Application)间的通信。AUTOSAR OS标准定义的IOC需与RTE进行交互,ORIENTAIS OS能够兼容有RTE与无RTE两种情况下的IOC通信。
IOC is a communication mechanism provided by the OS, enabling communication across cores, tasks, and partitions (OS-Applications). The IOC defined by the AUTOSAR OS standard requires interaction with RTE, and ORIENTAIS OS supports IOC communication both with and without RTE.
偏差(Deviation)¶
None
扩展(Expansion)¶
负载率监控(Load Rate Monitoring)¶
CPU负载率监控(CPU Load Rate Monitoring)¶
CPU负载率表示CPU在一段时间忙碌处理事务的时间占比。
CPU load rate represents the proportion of time the CPU spends busy processing transactions within a given period.
在任务切换或者中断进出的时候会记录当前运行的object(中断或任务)的执行时间。
The execution time of the currently running object (interrupt or task) is recorded during task switching or interrupt entry/exit.
在systimer中断中周期计算CPU的负载率。
The CPU load rate is periodically calculated in the systimer interrupt.
CPU负载率计算公式:CPU 负载率 = ( 单位时间 - 单位时间内 IDLE TASK 运行时间 ) / 单位时间 * 100%
CPU load rate calculation formula: CPU load rate = (Unit time - IDLE TASK running time within the unit time) / Unit time * 100%
对于用户来说,计算CPU负载率是无感的,用户只需要配置负载率监控功能之后查看Os_CpuLoadRatio变量即可。同时支持,最大负载、最小负载、平均负载的查看。
For users, CPU load rate calculation is transparent. Users only need to configure the load rate monitoring function and then check the Os_CpuLoadRatio variable. It also supports viewing maximum load, minimum load, and average load.
Task负载率监控(Task Load Rate Monitoring)¶
Task负载率表示CPU在一段时间内运行Task的时间占比。
Task load rate represents the proportion of time the CPU spends running a Task within a given period.
在Os_EnterTaskRecordTick或者Os_ExitTaskRecordTick的时候会记录当前运行的Task的执行时间。
The execution time of the currently running Task is recorded when Os_EnterTaskRecordTick or Os_ExitTaskRecordTick is called.
在systimer中断中周期计算Task的负载率。
The Task load rate is periodically calculated in the systimer interrupt.
Task负载率计算公式:TASK负载率 = ( 单位时间内 TASK运行时间 ) / 单位时间 * 100%
Task load rate calculation formula: Task load rate = (Task running time within unit time) / Unit time * 100%
对于用户来说,计算Task负载率是无感的,用户只需要配置负载率监控功能之后查看对应的Os_TaskLoadRatio[TaskID]变量即可。同时支持,最大负载、最小负载、平均负载的查看。
For users, Task load rate calculation is transparent. Users only need to configure the load rate monitoring function and then check the corresponding Os_TaskLoadRatio[TaskID] variable. It also supports viewing maximum load, minimum load, and average load.
ISR负载率监控(ISR Load Rate Monitoring)¶
ISR负载率表示CPU在一段时间内运行ISR的时间占比。
ISR load rate represents the proportion of time the CPU spends running ISRs within a given period.
在Os_EnterIsrRecordTick或者Os_ExitIsrRecordTick的时候会记录当前运行的ISR的执行时间。
The execution time of the currently running ISR is recorded when Os_EnterIsrRecordTick or Os_ExitIsrRecordTick is called.
在systimer中断中周期计算ISR的负载率。
The ISR load rate is periodically calculated in the systimer interrupt.
ISR负载率计算公式:ISR 负载率 = ( 单位时间内 ISR 运行时间 ) / 单位时间 * 100%
ISR load rate calculation formula: ISR load rate = (ISR running time within unit time) / Unit time * 100%
对于用户来说,计算ISR负载率是无感的,用户只需要配置负载率监控功能之后查看对应的Os_IsrLoadRatio[IsrID]变量即可。同时支持,最大负载、最小负载、平均负载的查看。
For users, ISR load rate calculation is transparent. Users only need to configure the load rate monitoring function and then check the corresponding Os_IsrLoadRatio[IsrID] variable. It also supports viewing maximum load, minimum load, and average load.
TaskResponseTime监控(TaskResponseTime Monitoring)¶
TaskResponseTime表示任务从开时运行到结束运行的绝对时间。
TaskResponseTime represents the absolute time from when a task starts running to when it finishes running.
在Os_TaskRecordStartTick开时记录Task的起始时间,在Os_TaskRecordTotalTick的时候会记录当前运行的ISR的执行时间。
The start time of the Task is recorded when Os_TaskRecordStartTick is called, and the execution time of the currently running ISR is recorded when Os_TaskRecordTotalTick is called.
TaskResponseTime = Task结束时间 - Task起始时间
TaskResponseTime = Task end time - Task start time
对于用户来说,计算TaskResponseTime是无感的,用户只需要配置Task监控功能之后查看对应的Os_TaskResponseTime[TaskID]变量即可。同时支持,最大时间、最小时间、平均时间的查看。
For users, TaskResponseTime calculation is transparent. Users only need to configure the Task monitoring function and then check the corresponding Os_TaskResponseTime[TaskID] variable. It also supports viewing maximum time, minimum time, and average time.
Os_InterLockTime监控 Os_InterLockTime(Monitoring)¶
Os_InterLockTime(关中断时长监控)用于Os_InitOsMonitor接口调用之后,监控所有中断(包括2类中断)或者2类中断的关闭时长。
Os_InterLockTime (interrupt disable duration monitoring) monitors the duration for which all interrupts (including Category 2 interrupts) or only Category 2 interrupts are disabled after the Os_InitOsMonitor interface is called.
用户调用接口SuspendAllInterrupts()、SuspendOSInterrupts()关中断时,中断监控模块开始统计所有中断类型或者2类中断类型的关中断时长;用户调用ResumeAllInterrupts()、ResumeOSInterrupts()恢复中断使能时,暂停所有中断类型或者2类中断类型的关中断时长统计,并更新计算结果。
When the user calls SuspendAllInterrupts() or SuspendOSInterrupts() to disable interrupts, the interrupt monitoring module starts counting the disable duration for all interrupt types or Category 2 interrupt types; when the user calls ResumeAllInterrupts() or ResumeOSInterrupts() to re-enable interrupts, the counting of disable duration for all interrupt types or Category 2 interrupt types is paused, and the calculation results are updated.
在systimer中断中周期计算关中断时间的在该周期时间的占比,用户可通过Os_InterTatio变量查看。
The proportion of interrupt disable time within the current cycle is periodically calculated in the systimer interrupt, which users can view through the Os_InterRatio variable.
对于用户来说,计算Os_InterLockTime是无感的,用户只需要配置监控功能之后查看对应的TopRecordTableHead、Os_InterRecordTable变量,即可查看最长关中断时间、最近关中断时间的记录情况。
For users, Os_InterLockTime calculation is transparent. Users only need to configure the monitoring function and then check the corresponding TopRecordTableHead and Os_InterRecordTable variables to view records of the longest interrupt disable time and the most recent interrupt disable time.
调度次数监控(Scheduling Count Monitoring)¶
Task调度监控(Task Scheduling Monitoring)¶
Task调度监控用于监控从StartOS起至当前时刻,各个Task的总调度次数。
Task scheduling monitoring tracks the total number of times each Task has been scheduled from StartOS initiation to the current moment.
用户需要配置监控功能,之后Os在调度函数中记录各个Task被触发的次数,用户可以调用Os_GetTaskScheduleCount来获取某个task的总调度次数。
Users need to configure the monitoring function. After configuration, the OS records the trigger count for each Task in the scheduling function, and users can call Os_GetTaskScheduleCount to obtain the total scheduling count for a specific task.
Note
某一个Task被打断后重新返回到该Task,也被视为产生了一次调度。
If a Task is interrupted and then returns to the same Task, it is also considered a scheduling occurrence.
Isr2调度监控 Isr2(Scheduling Monitoring)¶
Isr2调度监控用于监控从StartOS起至当前时刻,各个Isr2的总调度次数。
Isr2 scheduling monitoring tracks the total number of times each Isr2 has been scheduled from StartOS initiation to the current moment.
用户需要配置监控功能,之后Os在中断进入退出序言中记录Isr2被触发的次数,用户可以调用Os_GetIsr2ScheduleCount来获取某个Isr2被触发的次数。
Users need to configure the monitoring function. After configuration, the OS records the trigger count for Isr2 in the interrupt entry and exit prologues, and users can call Os_GetIsr2ScheduleCount to obtain the trigger count for a specific Isr2.
Note
某一Isr2被打断后重新返回到该Isr2,也被视为产生了一次调度
If an Isr2 is interrupted and then returns to the same Isr2, it is also considered a scheduling occurrence.
Event监控(Event Monitoring)¶
Event实时性监控 Event Real-time(Monitoring)¶
Event实时性监控用于监控从event被触发到task最终响应event的这段时间是否过长。
Event real-time monitoring checks whether the duration from event triggering to task response is excessively long.
在SetEvent中Os_MonitorEventStartTime中记录event被触发的时刻;
The event trigger timestamp is recorded in Os_MonitorEventStartTime within SetEvent;
在WaitEvent和WaitAllEvents中调用Os_MonitorEventEndTime记录响应截止时间;
The response deadline is recorded by calling Os_MonitorEventEndTime in WaitEvent and WaitAllEvents;
在ClearEvent中通过调用Os_MonitorEventResponseTime判断event响应时长是否大于等于配置门限,如果超出门限且配置HOOK则进入EventResponseTimeHook。
In ClearEvent, Os_MonitorEventResponseTime is called to determine if the event response duration meets or exceeds the configured threshold. If the threshold is exceeded and the HOOK is configured, EventResponseTimeHook is invoked.
Event响应率监控(Event Response Rate Monitoring)¶
Event响应率监控用于监控是否存在Event响应率过低的场景。
Event response rate monitoring detects scenarios where the event response rate is too low.
在SetEvent中Os_AddEventResponseNum记录event被触发的次数;
Os_AddEventResponseNum records the trigger count of an event in SetEvent;
在ClearEvent中通过调用Os_MonitorEventResponseRate判断event是否存在多次SetEvent对应一次ClearEvent的场景,如果存在且配置了HOOK则进入EventResponseRateHook。
In ClearEvent, Os_MonitorEventResponseRate is called to detect scenarios where multiple SetEvents correspond to a single ClearEvent for an event. If such a scenario is detected and the HOOK is configured, EventResponseRateHook is invoked.
集成(Integration)¶
操作步骤如下:
The operation steps are as follows:
选择ORIENTAIS配置工具OS模块中的选项并生成配置文件;
Select options in the OS module of the ORIENTAIS configuration tool and generate configuration files;
在IDE中创建新项目;
Create a new project in the IDE;
集成Os源码,配置文件和其他源文件;
Integrate Os source code, configuration files, and other source files;
构建项目以生成可执行文件。
Build the project to generate an executable file.
Caution
请参阅OS用户手册以获取ORIENTAIS配置工具OS模块的详细信息
Please refer to the OS user manual for detailed information about the ORIENTAIS configuration tool OS module
不同芯片平台生成的配置文件有些许差异,请参考芯片平台相关用户手册
Configuration files generated for different chip platforms may have slight variations. Please refer to the chip platform-specific user manual
文件列表(File List)¶
静态文件(Static Files)¶
文件(Files) |
描述(Description) |
|---|---|
Os.h |
公共头文件(Public header file) |
Os_Types.h |
类型定义头文件(Type definition header file) |
Os_Marcos.h |
宏定义头文件(Macro definition header file) |
Os_Kernel.c |
内核逻辑源代码(Kernel logic source code) |
Os_Internal.h |
内部头文件(Internal header file) |
Os_Alarm.c |
Alarm管理源文件(Alarm management source file) |
Os_Counter.c |
Counter管理源文件(Counter management source file) |
Os_Err.h |
错误管理头文件(Error management header file) |
Os_Event.c |
事件管理源文件(Event management source file) |
Os_Resource.c |
资源管理源文件(Resource management source file) |
Os_Task.c |
任务管理源文件(Task management source file) |
Os_ScheduleTable.c |
调度表管理源文件(Schedule table management source file) |
Os_Tprot.c |
时间保护源文件(Time protection source file) |
Os_Sprot.c |
服务保护源文件(Service protection source file) |
Os_Mprot.c |
内存保护源文件(Memory protection source file) |
Os_Appl.c |
OS-Application管理源文件(OS-Application management source file) |
Os_Spinlock.c |
Spinlock管理源文件(Spinlock management source file) |
Os_Core.c |
核控制操作源文件(Core control operation source file) |
Os_Rpc.c |
RPC管理源文件(RPC management source file) |
Os_Interrupt.c |
中断控制源文件(Interrupt control source file) |
Os_Peripheral.c |
外设访问功能源文件(Peripheral access function source file) |
Os_Ioc.c |
核间通信功能源文件(Inter-core communication function source file) |
Os_ECode.h |
系统服务错误类型头文件(System service error type header file) |
Os_Hook.c |
Hook功能源文件(Hook function source file) |
Os_StackMonitor.c |
栈监控源文件(Stack monitoring source file) |
Os_MemMap.h |
OS内存映射头文件(OS memory mapping header file) |
Os_Panic.c |
Panic管理源文件(Panic management source file) |
Os_Extend.h |
扩展接口头文件(内核)(Extension interface header file (kernel)) |
Platform |
请参考芯片相关的用户手册(Please refer to the chip-specific user manual) |
动态文件(Dynamic Files)¶
文件(File) |
描述(Description) |
|---|---|
Os_Cfg_s.h |
Os Cfg Asm Declarations |
Os_Cfg.c |
Os Cfg Data Definitions |
Os_Cfg.h |
Os Cfg define data Declarations |
Os_CfgData.h |
Os Cfg Data Declarations |
Os_CoreCfg.c |
Os Cfg Code Data Definitions |
Os_CoreCfg.h |
Os Cfg Code Data Declarations |
Os_DataSection.lsl |
Os app linck script |
Os_Intvet.c |
Os ISR install src |
Os_Kdata.c |
Os control data Definitions |
Os_Linklsl |
Os app data linck script |
Os_Mp_MemMap.h |
Os Memmap marcos Declarations |
Os_MprotCfg.c |
Os Memmap cfg data Definitions |
Os_MprotCfg.h |
Os Memmap cfg data Declarations |
Os_Trace.orti |
Os ORTI cfg Declarations |
Os_Userlnf.c |
Os Interface api Declarations |
错误处理(Error Handling)¶
None
接口描述(Interface Description)¶
Task(Functions)¶
ORIENTAIS OS提供两种类型的任务:
ORIENTAIS OS provides two types of tasks:
基本任务 Basic Task
拓展任务 Extended Task
拓展任务与基本任务的区别是,拓展任务允许使用系统服务WaitEvent,这可能会使任务进入Waiting状态。
The difference between an Extended Task and a Basic Task is that the Extended Task is allowed to use the system service WaitEvent, which may cause the task to enter the Waiting state.
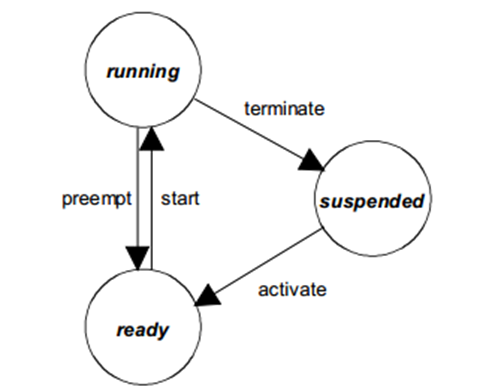
基本任务状态模型 (Basic Task State Model)¶
过度(Transition) |
历史状态(Previous State) |
新状态(New State) |
描述(Description) |
|---|---|---|---|
activate |
suspended |
ready |
系统服务将新任务设置为就绪状态。ORIENTAIS OS确保任务的执行将从第一条指令开始。(The system service sets the new task to the Ready state. ORIENTAIS OS ensures that the task execution starts from the first instruction.) |
start |
ready |
running |
执行调度器选择的就绪任务。 (Execute the ready task selected by the scheduler.) |
preempt |
running |
ready |
调度程序尝试启动另一个任务。正在运行的任务变为就绪状态。(通常是在低优先级任务的运行过程中,激活或者释放更高优先级任务) (The scheduler attempts to start another task. The currently running task transitions to the Ready state. (Typically, this occurs when a higher-priority task is activated or released during the execution of a lower-priority task.)) |
terminate |
running |
suspended |
正在运行的任务通过系统服务使其转变为挂起状态。(The running task transitions to the Suspended state via a system service.) |
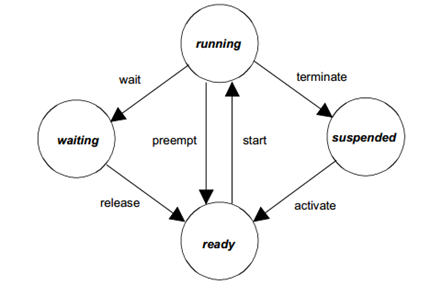
拓展任务状态模型(Extended Task State Model)¶
过度(Transition) |
历史状态(Previous State) |
新状态(New State) |
描述(Description) |
|---|---|---|---|
activate |
suspended |
ready |
系统服务将新任务设置为就绪状态。ORIENTAIS OS确保任务的执行将从第一条指令开始。 (The system service sets the new task to the Ready state. ORIENTAIS OS ensures that the task execution starts from the first instruction.) |
start |
ready |
running |
执行调度器选择的就绪任务。 (Execute the ready task selected by the scheduler.) |
wait |
running |
waiting |
过渡到等待状态是由系统服务引起的(例如:WaitEvent)。为了任务能够继续运行,需要为该任务设置一个它所等待的事件。(The transition to the Waiting state is triggered by a system service (e.g., WaitEvent). For the task to resume running, an event that the task is waiting for must be set for it.) |
release |
waiting |
ready |
设置至少一个任务等待的事件。(Set at least one event that the task waits for.) |
preempt |
running |
ready |
调度程序尝试启动另一个任务。正在运行的任务变为就绪状态。(通常是在低优先级任务的运行过程中,激活或者释放更高优先级任务)(The scheduler attempts to start another task. The currently running task transitions to the Ready state. (Typically, this happens when a higher-priority task is activated or released during the execution of a lower-priority task.)) |
terminate |
running |
suspended |
正在运行的任务通过系统服务使其转变为挂起状态。(The running task transitions to the Suspended state through a system service.) |
ActivateTask¶
StatusType ActivateTask(TaskType TaskID)
The task<TaskID> is transferred from the suspended state into the ready state.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
TaskID |
Task reference. |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error. |
E_OS_LIMIT |
The number of activations has exceeded the limit. |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid TaskID. |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment. |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend. |
E_OS_ACCESS |
Application state error/ No access to this object. |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running. |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal, or rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
waiting the execution result timeout. |
Example
Example.1
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
TASK(TaskInit)
{
StatusType ret;
ret = ActivateTask(Task0);
/* If the priority of Task0 is greater than TaskInit's, the ActivateTask is don't return directly, and Task0 start to execute. If not, ActivateTask return ‘E_OK’ and program execution continues*/
......
}
Example.2
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
Task0: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Activation Limit:1
TASK(TaskInit)
{
StatusType ret;
ret = ActivateTask(Task0);
/* ret = E_OK*/
ret = ActivateTask(Task0);
/* ret = E_OS_LIMIT */
......
}
Note
如果有多个激活请求,ActivateTask不会立即更改任务状态。如果任务不为挂起状态,任务的激活次数将被记录,并在之后执行激活。
If there are multiple activation requests, ActivateTask does not change the task state immediately. If the task is not in the Suspended state, the number of activations for the task is recorded and the activation is performed later.
ActivateTask激活一个与运行中的任务拥有相同内部资源的任务,该任务不会直接执行。
ActivateTask activates a task that shares the same internal resources as the currently running task; this task will not be executed directly.
激活任务后,激活计数将增加。如果激活计数超过配置的计数值,那么本次ActivateTask的调用无效。
After activating a task, the activation count increases. If the activation count exceeds the configured limit, the current call to ActivateTask is invalid.
TerminateTask¶
StatusType TerminateTask(void)
This service causes the termination of the calling task. The calling task is transferred from the running state into the suspended state.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
this |
function does not return in correct case |
E_OS_RESOURCE |
Resources are still occupied by tasks |
E_OS_SPINLOCK |
Spinlock are still occupied by tasks |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
Example
OsResource: Type:INTERNAL
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Resource:OsResource, Autostart:True
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL
Task1: Priority:3, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Resource:OsResource
TASK(TaskInit)
{
/*user code*/
ActivateTask(Task1);
/* TaskInit and Task1 own same internal resource OsResource, therefore Task1 don’t preempt TaskInit. */
ChainTask(Task0);
/*Task0 is activated. ChainTask release TaskInit’s internal resource, therefore Task1 executes firstly due to the highest priority, then Task0 executes. */
......
}
Note
严格禁止在未调用TerminateTask或ChainTask的情况下结束任务功能(请勿使用“ return”),并且可能会使系统处于不确定状态。
It is strictly prohibited to terminate a task function without calling TerminateTask or ChainTask (do not use “return”), as this may leave the system in an undefined state.
任务必须释放占用的标准资源后才能使用该服务。
A task must release the standard resources it occupies before using this service.
ChainTask¶
StatusType ChainTask(TaskType TaskID)
This service causes the termination of the calling task. After termination of the calling task a succeeding task <TaskID> is activated.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
TaskID |
Task reference |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
this |
function does not return in correct case |
E_OS_LIMIT |
The number of activations has exceeded the limit |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid TaskID |
E_OS_RESOURCE |
Resources are still occupied by tasks |
E_OS_SPINLOCK |
Spinlock are still occupied by tasks |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
Application state error/ No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal, or rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
waiting the execution result timeout. |
Example
OsResource: Type:INTERNAL
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Resource:OsResource, Autostart:True
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL
Task1: Priority:3, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Resource:OsResource
TASK(TaskInit)
{
/*user code*/
ActivateTask(Task1);
/* TaskInit and Task1 own same internal resource OsResource, therefore Task1 don’t preempt TaskInit. */
ChainTask(Task0);
/*Task0 is activated. ChainTask release TaskInit’s internal resource, therefore Task1 executes firstly due to the highest priority, then Task0 executes. */
......
}
Note
如果后续任务与当前任务相同,则不会导致多个请求。任务不会转移到挂起状态,但是会立即再次准备就绪。
If the subsequent task is the same as the current task, it will not result in multiple requests. The task will not transition to the Suspended state but will immediately become ready again.
即使后续任务与当前任务相同,分配给调用任务的内部资源也会自动释放。
Even if the subsequent task is the same as the current task, the internal resources allocated to the calling task are automatically released.
调用任务所占用的非内部资源应在调用ChainTask之前释放。
Non-internal resources occupied by the calling task should be released before calling ChainTask.
激活任务后,计数将增加。如果激活计数超过配置的计数,本次ChainTask调用无效。
After the task is activated, the count increases. If the activation count exceeds the configured limit, the current call to ChainTask is invalid.
Schedule¶
StatusType Schedule(void)
If a higher-priority task is ready , the internal resource of the task is released, the current task is put into the ready state, its context is saved and the highe r-priority task is executed. Otherwise the calling task is continued.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_RESOURCE |
Resources are still occupied by tasks |
E_OS_SPINLOCK |
Spinlock are still occupied by tasks |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
Example
OsResource: Type:INTERNAL
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Resource:OsResource, Autostart:True
Task1: Priority:3, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Resource:OsResource
TASK(TaskInit)
{
/*user code*/
ActivateTask(Task1);
/* TaskInit and Task1 own same internal resource OsResource, therefore Task1 don’t preempt TaskInit. */
Schedule();
/* Schedule release TaskInit’s internal resource, therefore Task1 executes. */
......
}
Note
该服务对分配了内部资源的任务有影响。
This service has an impact on tasks allocated with internal resources.
任务必须释放占用的非内部资源后才能调用。
The task must release any occupied non-internal resources before calling this service.
GetTaskID¶
StatusType GetTaskID(TaskRefType TaskID)
GetTaskID returns the information about the TaskID of the task which is currently running.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
TaskID |
Task reference |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal, or rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
ISR_0: Priority:101, Category:CATEGORY_2
TASK(TaskInit)
{
TaskType taskid;
StatusType ret;
ret = GetTaskID(&taskid);
/* ret = E_OK , taskid = TaskInit */
/* trigger interrupt ISR_0*/
......
}
ISR(ISR_0)
{
TaskType taskid;
StatusType ret;
ret = GetTaskID(&taskid);
/* ret = E_OK , taskid = TaskInit */
}
Note
当没有任务在运行时,“ TaskID”的值为INVALID_TASK。
When no task is running, the value of “TaskID” is INVALID_TASK.
GetTaskState¶
StatusType GetTaskState(TaskType TaskID, TaskStateRefType State)
Returns the state of a task (running, ready, waiting, suspended)at the time of calling GetTaskState.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
TaskID |
Task reference |
[out] |
State |
Status of the task |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid TaskID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
Application state error/ No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal, or rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
waiting the execution result timeout. |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL,
Task1: Priority:3, Preemptive Policy:FULL,
Task2: Priority:4, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Event: Event_0
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ActivateTask(Task0); /* step 1*/
......
}
TASK(Task0)
{
TaskStateType taskstate;
ActivateTask(Task2); /* step 2*/
/* step4*/
ret = GetTaskState(TaskInit,&taskstate);/*taskstate = TASK_STATE_READY*/
ret = GetTaskState(Task0,&taskstate); /*taskstate = TASK_STATE_RUNNING*/
ret = GetTaskState(Task1,&taskstate);/*taskstate = TASK_STATE_SUSPENDED*/
ret = GetTaskState(Task2,&taskstate); /*taskstate = TASK_STATE_WAITING*/
......
}
TASK(Task2)
{
WaitEvent(Event_0); /* step 3*/
......
}
Note
在完全抢占式系统中从任务进行调用时,返回时结果可能已经不正确。
When called from a task in a fully preemptive system, the result might already be incorrect by the time of return.
如果为某个任务(多次激活)调用服务,则如果该任务的任何实例正在运行,则状态将设置为“正在运行”。
If the service is called for a task (with multiple activations), and if any instance of that task is currently running, the state will be set to “running”.
ActivateTaskAsyn¶
StatusType ActivateTaskAsyn(TaskType TaskID)
Asynchronous version of the
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
TaskID |
Task reference |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_LIMIT |
The number of activations has exceeded the limit |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid TaskID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
Application state error/ No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal, or rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
waiting the execution result timeout. |
Example
C0_TaskInit(Core0): Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
C1_Task0(Core0): Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL
TASK(C0_TaskInit)
{
StatusType ret;
ret = ActivateTaskAsyn (C1_Task0);
......
}
Note
如果待激活的任务与当前任务不在同一个核,ActivateTaskAsyn()采用异步的方式激活该任务。
If the task to be activated is not on the same core as the current task, ActivateTaskAsyn() activates the task asynchronously.
Interrupt(Functions)¶
处理中断的函数(中断服务程序:ISR)分为两类中断:
Functions that handle interrupts (Interrupt Service Routines: ISRs) are categorized into two types:
1类中断: 此类中断不使用操作系统服务。中断结束后,程序将在发生中断位置继续执行,即中断对任务管理没有影响。此类别的中断具有最小的开销。
Type 1 Interrupts: These interrupts do not use operating system services. After the interrupt ends, the program resumes execution from the point of interruption, meaning the interrupt has no impact on task management. Interrupts in this category have minimal overhead.
2类中断: Os提供一个中断框架,为特定的用户程序提供运行环境。这类中断能够使用Os的系统服务。
Type 2 Interrupts: The OS provides an interrupt framework that offers an execution environment for specific user programs. This type of interrupt can use the OS system services.
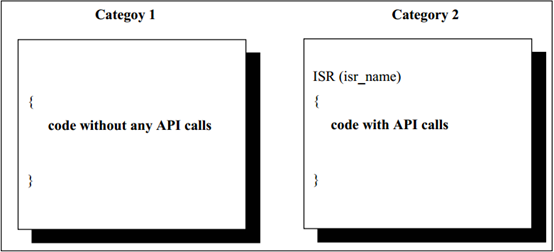
ORIENTAIS OS的ISR类别 (ISR Types of ORIENTAIS OS)¶
EnableAllInterrupts¶
void EnableAllInterrupts(void)
This service restores the state saved by DisableAllInterrupts.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
void
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
TASK(TaskInit)
{
DisableAllInterrupts();
/*user action except system service*/
EnableAllInterrupts();
......
}
Note
该服务与DisableAllInterrupts服务相对应,后者必须在之前被调用,其目的是保障代码临界区的完整性。
This service corresponds to the DisableAllInterrupts service, which must be called beforehand to ensure the integrity of the code critical section.
DisableAllInterrupts¶
void DisableAllInterrupts(void)
This service disables all interrupts for which the hardware supports disabling. The state before is saved for the EnableAllInterrupts call.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
void
Note
主要用于某些不能使用ORIENTAIS OS API的临界段。
Mainly used for certain critical sections where the ORIENTAIS OS API cannot be used.
ResumeAllInterrupts¶
void ResumeAllInterrupts(void)
This service restores t he recognition status of all interrupts saved by the SuspendAllInterrupts service.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
void
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
void function_0()
{
SuspendAllInterrupts();
/*user action except system service*/
ResumeAllInterrupts();
}
TASK(TaskInit)
{
SuspendAllInterrupts();
/*user action except system service*/
ResumeAllInterrupts();
SuspendAllInterrupts();
/*user action except system service*/
function_0(); /*nested using*/
ResumeAllInterrupts();
......
}
Note
SuspendAllInterrupts / ResumeAllInterrupts可以嵌套使用。如果嵌套调用SuspendAllInterrupts和ResumeAllInterrupts,SuspendAllInterrupts第一次调用时保存的中断识别状态将在ResumeAllInterrupts最后一次调用时恢复。
SuspendAllInterrupts / ResumeAllInterrupts can be used in a nested manner. If SuspendAllInterrupts and ResumeAllInterrupts are called nestedly, the interrupt recognition state saved during the first call of SuspendAllInterrupts will be restored during the last call of ResumeAllInterrupts.
SuspendAllInterrupts¶
void SuspendAllInterrupts(void)
This service saves the re cognition status of all interrupts and disables all interrupts for which the hardware supports.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
void
Note
主要用于某些不能使用ORIENTAIS OS API的临界段。
Mainly used for certain critical sections where the ORIENTAIS OS API cannot be used.
ResumeOSInterrupts¶
void ResumeOSInterrupts(void)
This service restores the recognition status of interrupts saved by the SuspendOSInterrupts service.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
void
Note
SuspendOSInterrupts / ResumeOSInterrupts可以嵌套使用。如果嵌套调用SuspendOSInterrupts和ResumeOSInterrupts,SuspendOSInterrupts的第一次调用时保存的中断识别状态将在ResumeAllInterrupts最后一次调用时恢复。
SuspendOSInterrupts / ResumeOSInterrupts can be used in a nested manner. If SuspendOSInterrupts and ResumeOSInterrupts are called nestedly, the interrupt recognition state saved during the first call of SuspendOSInterrupts will be restored during the last call of ResumeOSInterrupts.
SuspendOSInterrupts / ResumeOSInterrupts仅对2类中断有影响。
SuspendOSInterrupts / ResumeOSInterrupts only affect Category 2 Interrupts.
SuspendOSInterrupts¶
void SuspendOSInterrupts(void)
This service saves the recognition status of interrupts of category 2 and disables the recognition of these interrupts.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
void
Note
主要用于某些不能使用ORIENTAIS OS API的临界段。
Mainly used for certain critical sections where the ORIENTAIS OS API cannot be used.
GetISRID¶
ISRType GetISRID(void)
This service returns the identifier of the currently executing ISR.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
ISRType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
Returns |
the ID of CATEGORY_2 interrupt |
INVALID_ISR |
Example
App0: Trusted
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
ERAY_INT0: Priority:101, Category: CATEGORY_2
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ISRType isr;
/* OS_REG32(OS_SRC_ERAY_INT0_ADDR)) |= 0x04000000*/
TriggerInterrupt(OS_SRC_ERAY_INT0_ADDR);
ISRType isr;
isr = GetISRID();
/* isr = OS_ISR_INVALID */
}
ISR(ERAY_INT0)
{
ISRType isr;
isr = GetISRID();
/* isr = CFG_ISR_ERAY_INT0_ID */
}
EnableInterruptSource¶
StatusType EnableInterruptSource(ISRType ISRID, boolean ClearPending)
Enables the interrupt source by modifying the interrupt controller registers. Additionally it may clear the interrupt pending flag.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ISRID |
The ID of a category 2 ISR. |
[in] |
ClearPending |
Whether to clear the interrupt pending flag. |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No error |
E_OS_NOFUNC |
EnableInterruptSource is called for an interrupt source which is already enabled. |
E_OS_ID |
ISRID is not a valid category 2 ISR identifier. |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong call context of the API function |
E_OS_ACCESS |
The calling application is not the owner of the ISR passed in ISRID |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
TASK(TaskInit)
{
……
StatusType ret;
ret = DisableInterruptSource(CFG_ISR_DMA_SF_DMA0_CH_10_ID);
……
ret = EnableInterruptSource(CFG_ISR_DMA_SF_DMA0_CH_10_ID, TRUE);
……
}
Note
该服务为了短时间屏蔽特定的中断或在特定时间内忽略特定源的中断请求。
This service is used to mask specific interrupts for a short duration or ignore interrupt requests from specific sources within a specified time period.
DisableInterruptSource¶
StatusType DisableInterruptSource(ISRType ISRID)
Disables the interrupt source by modifying the interrupt controller registers.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ISRID |
The ID of a category 2 ISR. |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No error |
E_OS_NOFUNC |
DisableInterruptSource is called for an interrupt source which is already disabled. |
E_OS_ID |
ISRID is not a valid category 2 ISR identifier. |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong call context of the API function |
E_OS_ACCESS |
The calling application is not the owner of the ISR passed in ISRID |
ClearPendingInterrupt¶
StatusType ClearPendingInterrupt(ISRType ISRID)
Clears the interrupt pending flag by modifying the interrupt controller registers.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ISRID |
The ID of a category 2 ISR. |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No error |
E_OS_ID |
ISRID is not a valid category 2 ISR identifier. |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong call context of the API function |
E_OS_ACCESS |
The calling application is not the owner of the ISR passed in ISRID |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
TASK(TaskInit)
{
……
StatusType ret;
ret = DisableInterruptSource(CFG_ISR_DMA_SF_DMA0_CH_10_ID);
……
ret = ClearPendingInterrupt(CFG_ISR_DMA_SF_DMA0_CH_10_ID);
……
}
Note
该服务为了短时间屏蔽特定的中断或在特定时间内忽略特定源的中断请求。
This service is used to mask specific interrupts for a short duration or ignore interrupt requests from specific sources within a given time frame.
Counter(Functions)¶
一个计数器由一个以“滴答”为单位表示的计数器值和一些计数器特定的常数。 Os提供标准化的API,以直接操作计数器。 Os提供了两种不同的计数器:
A counter consists of a counter value represented in “tick” units and some counter-specific constants. The OS provides standardized APIs to directly manipulate counters. The OS offers two distinct types of counters:
硬件Counter(Hardware Counter)
软件Counter(Software Counter)
硬件Counter: 由硬件(例如定时器)增加计数器的计数值。计数值由外围设备“在硬件中”维护。
Hardware Counter: The counter value is incremented by hardware (e.g., a timer). The counter value is maintained “in hardware” by peripheral devices.
软件Counter: 通过调用IncrementCounter增加计数器的计数值。计数值由ORIENTAIS OS “在软件中”维护。
Software Counter: The counter value is incremented by calling IncrementCounter. The counter value is maintained “in software” by ORIENTAIS OS.
IncrementCounter¶
StatusType IncrementCounter(CounterType CounterID)
This service increments a software counter.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
CounterID |
Counter Identifier |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No errors |
E_OS_ID |
CounterID is invalid or the counter implemented by hardware cannot be incremented by software |
E_OS_CORE |
The object is not belong to local core |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
Example
Alarm_10ms: ActivateTask: Task_10ms, CycleTime:10ms, Autostart:True
Task_10ms: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL
Counter_0: CounterType:SOFTWARE
TASK(Task_10ms)
{
IncrementCounter(Counter_0); /*The current tick value of Counter_0 increases 1*/
}
Note
该函数不能增加硬件计数器的计数值。
This function cannot increment the count value of a hardware counter.
GetCounterValue¶
StatusType GetCounterValue(CounterType CounterID, TickRefType Value)
This service reads the current count value of a counter .
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
CounterID |
Counter Identifier |
[out] |
Value |
Counter’s current clock value |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No errors |
E_OS_ID |
CounterID is invalid |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal, or rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_VALUE |
Parameter address is invalid |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
waiting the execution result timeout. |
Example
Alarm_10ms: ActivateTask: Task_10ms, CycleTime:10ms, Autostart:True
Task_10ms: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL
Counter_0: CounterType:SOFTWARE
Counter_1: CounterType:HARDWARE
TASK(Task_10ms)
{
TickType tick;
IncrementCounter(Counter_0);
/*The software counter need to increse by calling IncrementCounter.*/
GetCounterValue(Counter_0,&tick); /*The current tick value of Counter_0*/
GetCounterValue(Counter_1,&tick); /*The current tick value of Counter_1*/
}
Note
如果计数器是由硬件驱动的,则返回硬件计数器的计数值;如果计数器是由软件驱动的,则返回软件计数器的计数值。
If the counter is hardware-driven, it returns the hardware counter’s count value; if the counter is software-driven, it returns the software counter’s count value.
GetElapsedValue¶
StatusType GetElapsedValue(CounterType CounterID, TickRefType Value, TickRefType ElapsedValue)
This service gets the number of ticks between the current tick value and a previously read tick value.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
CounterID |
Counter Identifier |
[out] |
Value |
The current value of the counter (used as the next starting value) |
[out] |
ElapsedValue |
Interval between current clock value and start value |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No errors |
E_OS_ID |
CounterID is invalid |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal, or rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_VALUE |
Parameter address is invalid |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
waiting the execution result timeout. |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
Counter_0: CounterType:SOFTWARE, MaxTick:1000,MinTick:1
TASK(TaskInit)
{
TickType tick0,tick1,tick2;
IncrementCounter(Counter_0); /* the count of calling IncrementCounter is n.*/
tick0 = 5;
GetElapsedValue(Counter_0,&tick0,&tick1);
GetCounterValue(Counter_0,&tick2);
/* tick1 = ((n + 1000) – tick0(5)) % 1000 = n - 5, tick0 = tick2 = 10*/
......
}
Resource(Functions)¶
资源管理用于协调具有不同优先级的多个任务对共享资源的并发访问,例如:管理的实体(调度器),程序,内存或硬件区域。
Resource management is used to coordinate concurrent access by multiple tasks with different priorities to shared resources, such as managed entities (schedulers), programs, memory areas, or hardware regions.
在系统生成时,会为每个资源静态分配其自己的最高优先级。用户可以通过在任务/中断中调用GetResource / ReleaseResource来获取/释放标准资源。运行任务/中断的优先级暂时设置为资源的优先级,直到释放资源为止。
During system generation, each resource is statically assigned its own highest priority. Users can acquire/release standard resources by calling GetResource/ReleaseResource in tasks/interrupts. The priority of the running task/interrupt is temporarily elevated to the resource’s priority until the resource is released.
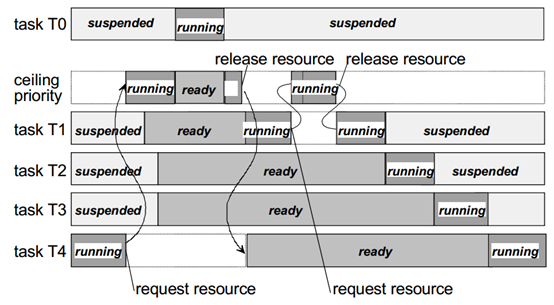
可抢占任务间优先级天花板的资源分配 (Resource Allocation with Priority Ceiling Among Preemptive Tasks)¶
内部资源是用户不可见的资源,因此系统功能GetResource和ReleaseResource无法操作内部资源。它们在一组明确定义的系统功能内部严格管理。除此之外,内部资源的行为与标准资源完全相同。
Internal resources are invisible to users; therefore, the system functions GetResource and ReleaseResource cannot operate on internal resources. They are strictly managed within a well-defined set of system functions. Apart from this, internal resources behave identically to standard resources.
占用标准资源时,不得调用TerminateTask,ChainTask,Schedule,WaitEvent。中断服务程序不应在占据资源的情况下结束。
When holding standard resources, TerminateTask, ChainTask, Schedule, and WaitEvent must not be called. Interrupt Service Routines (ISRs) should not terminate while holding resources.
GetResource¶
StatusType GetResource(ResourceType ResID)
This call serves to enter critical sections in the code that are assigned to the resource referenced by <ResID>. A critical section shall always be left using ReleaseResource.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ResID |
Resource Identifier |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid ResID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
Attempt to obtain a resource that has been occupied by a task, interrupt, or statically assigned to a ceiling priority task or an interrupt higher than the ceiling priority |
Example
Example.1
OsResource: Type:STANDARD
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True, Resource:OsResource
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Resource:OsResource
TASK(TaskInit)
{
GetResource(OsResource);
/* user code*/
ReleaseResource(OsResource);/*If a task don’t release resource occupied, it cannot activate other tasks configuring the resource and terminate itself.*/
ActivateTask(Task0);
......
}
Example.2
OsResource: Type:STANDARD
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True, Resource:OsResource
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Resource:OsResource
TASK(TaskInit)
{
GetResource(OsResource);
ActivateTask(Task0);
ReleaseResource(OsResource); /* The ReleaseResource can make OS scheduling. Task0 start to execute immediately.*/
......
}
Note
同一资源不能嵌套获取。用户可以多次获得不同的资源,并且以后进先出(LIFO)的顺序进行操作。
The same resource cannot be acquired in a nested manner. Users can acquire different resources multiple times and operate on them in Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) order.
建议对GetResource和ReleaseResource的调用尽可能出现在同一函数中。
It is recommended that calls to GetResource and ReleaseResource appear within the same function whenever possible.
任务获取资源后,系统不允许为不可抢占任务的发起重调度的服务(例如:TerminateTask,ChainTask,Schedule和WaitEvent)。
After a task acquires a resource, the system does not allow services that trigger rescheduling for non-preemptive tasks (e.g., TerminateTask, ChainTask, Schedule, and WaitEvent).
ReleaseResource¶
StatusType ReleaseResource(ResourceType ResID)
ReleaseResource is the counterpart of GetResource and serves to leave critical sections in the code that are assigned to the resource referenced by <ResID>.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ResID |
Resource Identifier |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid ResID |
E_OS_NOFUNC |
Attempt to release unused resources / Task/ISR don’t release resource and spinlock in nest order |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
An attempt was made to release a resource with a lower ceiling priority than a task that calls a task or interrupts a static configuration. |
E_OS_CORE |
The object is not belong to local core |
Note
资源释放者可以与资源获取者不同。
The resource releaser can be different from the resource acquirer.
Alarm(Functions)¶
Os提供用于处理重复事件的服务,例如在Alarm到期时激活任务,设置事件或调用AlarmCallBack回调函数。Alarm回调函数是应用程序提供的简短函数。
The OS provides services for handling recurring events, such as activating tasks upon alarm expiration, setting events, or invoking the AlarmCallback function. The alarm callback is a short function supplied by the application.
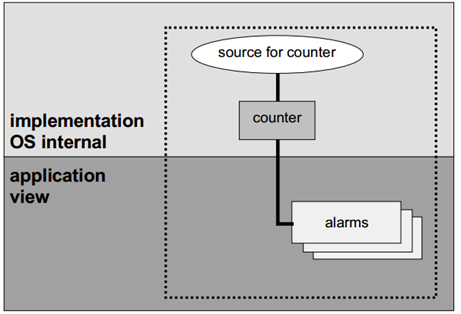
管理Alarm的分层模型 (Hierarchical Model for Alarm Management)¶
Counter和Alarm是静态定义的。Counter到Alarm的分配以及Alarm到期时要执行的具体操作也是静态定义的。
Counters and alarms are statically defined. The assignment of counters to alarms and the specific actions to be executed upon alarm expiration are also statically defined.
动态参数是Alarm到期时的计数器值,以及周期性Alarm的周期时间。
Dynamic parameters include the counter value at alarm expiration and the cycle time for periodic alarms.
GetAlarmBase¶
StatusType GetAlarmBase(AlarmType AlarmID, AlarmBaseRefType Info)
The system service GetAlarmBase reads the alarm base characteristics. The return value <Info> is a structure in which the information of data type
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
AlarmID |
Alarm Identifier |
[out] |
Info |
Information pointing to AlarmID alarms |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid AlarmID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal, or rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
Waiting the execution result timeout. |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
Counter_0: MaxTick:1000, MinTick:1, SecondsPerTick:0.001
Alarm_0: Counter: Counter_0
typedef struct
{
Os_TickType maxallowedvalue;
Os_TickType ticksperbase;
Os_TickType mincycle;
} Os_AlarmBaseType;
TASK(TaskInit)
{
AlarmBaseType alarmbase;
GetAlarmBase(Alarm_0,&alarmbase);
/* alarmbase. maxallowedvalue = MaxTick */
/* alarmbase. mincycle = MinTick */
/* alarmbase. ticksperbase = SecondsPerTick */
......
}
GetAlarm¶
StatusType GetAlarm(AlarmType AlarmID, TickRefType Tick)
The system service GetAlarm returns the relative value in ticks before the alarm <AlarmID> expires.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
AlarmID |
Alarm Identifier |
[in] |
Tick |
Relative number of ticks before the alarm is triggered |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_NOFUNC |
alarm is not used |
E_OS_ID |
invalid AlarmID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal, or rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
Waiting the execution result timeout. |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
Counter_0: CounterType: SOFTWARE, SecondsPerTick:0.001,
MaxTick:1000, MinTick:1
Alarm_0: Counter: Counter_0
TASK(TaskInit)
{
TickType tick;
/* alarm is not acitve. */
ret = GetAlarm(Alarm_0,&tick); /*ret = E_OS_NOFUNC */
SetRelAlarm(Alarm_0,100,0);
/* alarm is acitve. */
IncrementCounter(Counter_0); /* Execute [n] times */
ret = GetAlarm(Alarm_0,&tick); /*ret = E_OK, tick = [n]*/
......
}
Note
如果<AlarmID>没有定义,则<Tick>指向的内容不会改变。
If <AlarmID> is not defined, the content pointed to by <Tick> remains unchanged.
SetRelAlarm¶
StatusType SetRelAlarm(AlarmType AlarmID, TickType increment, TickType cycle)
The system service occupies the alarm <AlarmID> element. After <increment> ticks have elapsed, the task assigned to the alarm <AlarmID> is activated or the assigned event (only for extended tasks) is set or the alarm-callback routine is called.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
AlarmID |
Alarm Identifier |
[in] |
increment |
the number of clocks triggered for the first time relative to the current number of clocks |
[in] |
cycle |
The period of the alarm (Tick number), the cycle value of a single alarm is 0 |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_STATE |
Alarm corresponding to AlarmID is in use |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid AlarmID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_VALUE |
Increment value is not within the normal range (less than 0 or greater than maxallowedvalue) or Cycle value is not equal to 0 and is not within the allowed count range (less than mincycle or greater than maxallowedvalue) |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
Waiting the execution result timeout. |
Note
预设时间到期,将根据配置情况触发相关服务,例如:激活任务,设置事件,回调等。
When the preset time expires, relevant services are triggered based on the configuration, such as task activation, event setting, and callback execution.
如果相对时间为零,将立即触发相关服务。
If the relative time is zero, the relevant services are triggered immediately.
SetAbsAlarm¶
StatusType SetAbsAlarm(AlarmType AlarmID, TickType start, TickType cycle)
The system service occupies the alarm <AlarmID> element. When <start> ticks are reached, the task assigned to the alarm <AlarmID> is activated or the assigned event (only for extended tasks) is set or the alarm-callback routine is called.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
AlarmID |
Alarm Identifier |
[in] |
start |
Number of absolute clocks triggered for the first time |
[in] |
cycle |
The period of the alarm (Tick number), the cycle value of a single alarm is 0 |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_STATE |
Alarm is active |
E_OS_ID |
invalid AlarmID |
E_OS_VALUE |
Increment value is not within the normal range (less than 0 or greater than maxallowedvalue) or Cycle value is not equal to 0 and is not within the allowed count range (less than mincycle or greater than maxallowedvalue) |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
Waiting the execution result timeout. |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL
Counter_0: MaxTick:1000, MinTick:1, CounterType: SOFTWARE
Alarm_0: Counter: Counter_0 ActivateTask:Task0
TASK(TaskInit)
{
IncrementCounter(Counter_0);/*1*/
SetAbsAlarm(Alarm_0,2,0);
IncrementCounter(Counter_0);/*2*/
......
}
TASK(TaskInit)
{
/* step 2*/
}
Note
预设时间到期,将根据配置情况触发相关服务,例如:激活任务,设置事件,回调等。
When the preset time expires, relevant services are triggered according to the configuration, such as task activation, event setting, and callback execution.
如果绝对时间等于或接近当前时间,将立即触发相关服务。
If the absolute time equals or is close to the current time, the relevant services are triggered immediately.
如果绝对时间已过,相关服务将在下次到达时触发。
If the absolute time has passed, the relevant services are triggered upon the next occurrence.
CancelAlarm¶
StatusType CancelAlarm(AlarmType AlarmID)
The system service cancels the alarm <AlarmID>.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
AlarmID |
Alarm Identifier |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_NOFUNC |
Alarm is not used |
E_OS_ID |
invalid AlarmID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
Waiting the execution result timeout. |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
Counter_0: CounterType: SOFTWARE
Alarm_0: Counter: Counter_0
TASK(TaskInit)
{
StatusType ret;
TickType tick;
/* alarm is not acitve. */
ret = GetAlarm(Alarm_0,&tick); /*ret = E_OS_NOFUNC */
ret = SetRelAlarm(Alarm_0,100,0); /*ret = E_OK*/
/* alarm is acitve. */
ret = GetAlarm(Alarm_0,&tick); /*ret = E_OK*/
ret = CancelAlarm(Alarm_0); /*ret = E_OK*/
/* alarm is not acitve. */
ret = GetAlarm(Alarm_0,&tick); /*ret = E_OS_NOFUNC */
......
}
Event(Functions)¶
事件机制(Event Mechanism):
是一种同步手段
It is a synchronization mechanism.
仅拓展任务可用
Only extended tasks can use events.
Figure解释了在完全抢占式调度的情况下通过设置事件使扩展任务的同步,其中扩展任务T1具有更高的优先级。
The figure illustrates the synchronization of extended tasks through event setting under fully preemptive scheduling, where extended task T1 has a higher priority.
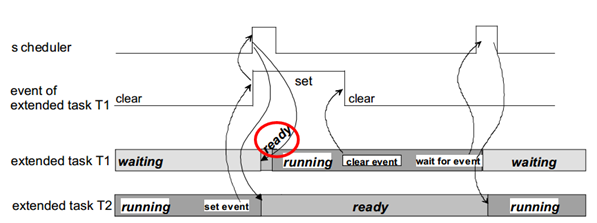
可抢占扩展任务的同步 (Synchronization of Preemptible Extended Tasks)¶
SetEvent¶
StatusType SetEvent(TaskType TaskID, EventMaskType Mask)
The events of task <TaskID> are set according to the event mask <Mask>. Calling SetEvent causes the task <TaskID> to be transferred to the ready state, if it was waiting for at least one of the events specified in <Mask>.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
TaskID |
Task reference |
[in] |
Mask |
Event mask, the configured event name |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid TaskID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
Task is not an extended task / No access to this object |
E_OS_STATE |
event cannot be set when the task is suspended |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal, or rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
waiting the execution result timeout. |
Note
事件的状态以’位’为单位,事件中未设置的位保持不变。
The state of an event is measured in bits, and unset bits within the event remain unchanged.
任务可以自行设置事件。
A task can set events autonomously.
在ECC1,ECC2下有效。
Valid under ECC1 and ECC2.
ClearEvent¶
StatusType ClearEvent(EventMaskType Mask)
The events of the extended task calling ClearEvent are cleared according to the event mask <Mask>.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Mask |
Event mask, the configured event name |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid TaskID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
Task is not an extended task |
Note
仅拓展任务可用。
Only extended tasks can use this feature.
在ECC1,ECC2下有效。
This is valid under ECC1 and ECC2.
GetEvent¶
StatusType GetEvent(TaskType TaskID, EventMaskRefType Event)
This service returns the current state of all event bits of the task <TaskID>, not the events that the task is waiting for.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
TaskID |
Task reference |
Event |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid TaskID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
Task is not an extended task |
E_OS_STATE |
task is suspended |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal, or rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
Note
用户可以获取当前正在运行的任务的事件。
Users can retrieve the events of the currently running task.
在ECC1,ECC2下有效。
This operation is valid under ECC1 and ECC2.
WaitEvent¶
StatusType WaitEvent(EventMaskType Mask)
The state of the calling task is set to waiting, unless at least one of the events specified in <Mask> has already been set.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Mask |
Event mask, the configured event name |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
this |
function does not return in correct case |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
Task is not an extended task |
E_OS_RESOURCE |
Resources are still occupied by tasks |
E_OS_SPINLOCK |
Spinlock are still occupied by tasks |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Event:Event_0
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ActivateTask(Task0); /* step 1*/
SetEvent(Task0,Event_0);/* step 3: Task state from waiting to running*/
......
}
TASK(Task0)
{
EventMaskType eventmask;
GetEvent(Task0, &eventmask);/* eventmask & Event_0 = 0 */
WaitEvent(Event_0); /* step 2: Task state from running to waiting*/
GetEvent(Task0, &eventmask);/* eventmask & Event_0 = Event_0 */
WaitEvent(Event_0); /* step 4: Task continues execute because the bit of event don’t be cleared. */
GetEvent(Task0, &eventmask);/* eventmask & Event_0 = Event_0 */
ClearEvent(Event_0); /* step 5*/
GetEvent(Task0, &eventmask);/* eventmask & Event_0 = 0 */
......
}
Note
在ECC1,ECC2下有效。
This service is valid under ECC1 and ECC2.
仅拓展任务可用。
Only extended tasks can use this service.
如果等待的事件未被设置,则当前任务进入等待状态并进行任务切换。如果等待的事件已被设置,则继续执行当前任务。
If the waited event is not set, the current task enters the waiting state and a task switch occurs. If the waited event is already set, the current task continues execution.
调用前必须释放占据的资源。
Occupied resources must be released before invocation.
设置的事件不会被主动清除。用户必须调用ClearEvent来清除事件。
Set events are not automatically cleared. Users must call ClearEvent to clear events.
WaitAllEvents¶
StatusType WaitAllEvents(EventMaskType Mask)
The state of the calling task is set to waiting, must all the events specified in <Mask> has already been set.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Mask |
Event mask, the configured event name |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
this |
function does not return in correct case |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
Task is not an extended task |
E_OS_RESOURCE |
Resources are still occupied by tasks |
E_OS_SPINLOCK |
Spinlock are still occupied by tasks |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Event:Event_0
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ActivateTask(Task0); /* step 1*/
SetEvent(Task0,Event_0 | Event_1);/* step 3: Task state from waiting to running*/
......
}
TASK(Task0)
{
EventMaskType eventmask;
GetEvent(Task0, &eventmask);/* eventmask & Event_0 = 0 */
WaitAllEvents(Event_0 | Event_1); /* step 2: Task state from running to waiting*/
GetEvent(Task0, &eventmask);/* eventmask & Event_0 = Event_0 */
WaitEvent(Event_0); /* step 4: Task continues execute because the bit of event don’t be cleared. */
GetEvent(Task0, &eventmask);/* eventmask & Event_0 = Event_0 */
ClearEvent(Event_0 | Event_1); /* step 5*/
GetEvent(Task0, &eventmask);/* eventmask & Event_0 = 0 */
......
}
SetEventAsyn¶
StatusType SetEventAsyn(TaskType TaskID, EventMaskType Mask)
Asynchronous version of the
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
TaskID |
Task reference |
[in] |
Mask |
Event mask, the configured event name |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid TaskID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
Task is not an extended task / No access to this object |
E_OS_STATE |
event cannot be set when the task is suspended |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal, or rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
waiting the execution result timeout. |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Event:Event_0
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ActivateTask(Task0); /* step 1*/
SetEventAsyn(Task0,Event_0 | Event_1);/* step 3: Task state from waiting to running*/
......
}
TASK(Task0)
{
EventMaskType eventmask;
GetEvent(Task0, &eventmask);/* eventmask & Event_0 = 0 */
WaitAllEvents(Event_0 | Event_1); /* step 2: Task state from running to waiting*/
GetEvent(Task0, &eventmask);/* eventmask & Event_0 = Event_0 */
WaitEvent(Event_0); /* step 4: Task continues execute because the bit of event don’t be cleared. */
GetEvent(Task0, &eventmask);/* eventmask & Event_0 = Event_0 */
ClearEvent(Event_0 | Event_1); /* step 5*/
GetEvent(Task0, &eventmask);/* eventmask & Event_0 = 0 */
......
}
ScheduleTable(Functions)¶
调度表类似于使用Counter和一系列自动启动的Alarms来实现静态定义的任务激活机制。
A schedule table is analogous to a statically defined task activation mechanism implemented using a Counter and a series of auto-started Alarms.
调度表提供了一组静态定义的溢出点封装。每个溢出点定义:
A schedule table provides a set of statically defined expiry point encapsulations. Each expiry point defines:
处理溢出点时,将执行动作(通过ORIENTAIS配置工具OS模块配置)。动作是任务的激活或事件的设置。
When processing the expiry point, an action (configured via the OS module of the ORIENTAIS configuration tool) is executed. The action is either task activation or event setting.
从调度表的开始处以”滴答”为单位的偏移量。
An offset in “tick” units from the start of the schedule table.
在运行时,ORIENTAIS OS将遍历调度表,依次处理每个溢出点。调度表由一个计数器驱动。计数器的属性会影响调度表中允许配置的内容。
During runtime, ORIENTAIS OS traverses the schedule table and processes each expiry point sequentially. The schedule table is driven by a counter, and the counter’s properties affect the configurable content within the schedule table.
用户可以为调度表设置为同步模式。ORIENTAIS OS通过两种方式提供对同步的支持:
Users can configure the schedule table for synchronous mode. ORIENTAIS OS provides synchronization support in two ways:
隐式同步:驱动调度表的计数器要求是同步计数器。这通常是采用时间触发的网络技术(例如FlexRay,TTP)实现同步的方式-底层硬件管理网络时间同步,并简单地将时间显示为ORIENTAIS OS的输出/比较计时器接口。Figure显示了隐式同步调度表可能出现的状态。
Implicit Synchronization: The counter driving the schedule table must be a synchronous counter. This is typically implemented using time-triggered network technologies (e.g., FlexRay, TTP) — the underlying hardware manages network time synchronization and presents the time simply as an output/compare timer interface to ORIENTAIS OS. The figure shows possible states of an implicitly synchronized schedule table.
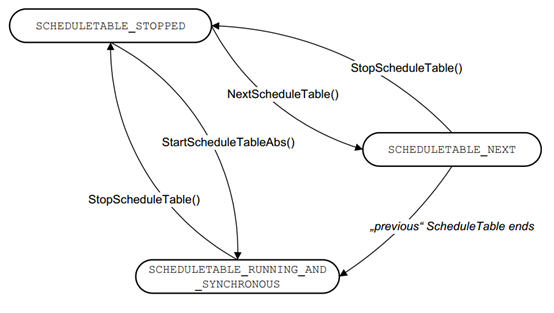
隐式同步调度表的状态 (States of Implicitly Synchronized Schedule Table)¶
显式同步:调度表由ORIENTAIS OS计数器驱动,而不要求是同步的计数器。ORIENTAIS OS还提供一些其他功能,以使其计数器驱动的调度表与同步计数器同步。通常,这是与定期广播全局时间进行同步的方式。Figure显示了显式同步调度表可能出现的状态。
Explicit Synchronization: The schedule table is driven by an ORIENTAIS OS counter, which is not required to be synchronous. ORIENTAIS OS also provides additional functions to synchronize its counter-driven schedule table with a synchronous counter. Typically, this synchronizes with a periodically broadcast global time. The figure shows possible states of an explicitly synchronized schedule table.
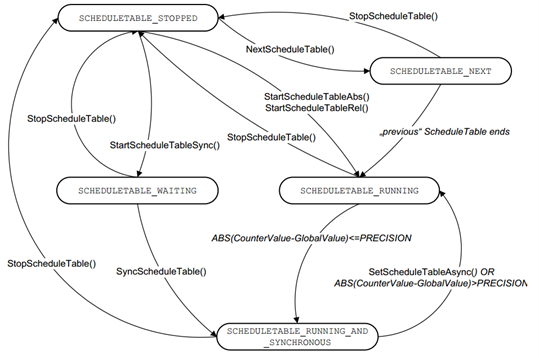
显式同步调度表的状态(图中未显示所有的跳转条件) (States of Explicitly Synchronized Schedule Table - Not all transition conditions are shown)¶
StartScheduleTableRel¶
StatusType StartScheduleTableRel(ScheduleTableType ScheduleTableID, TickType Offset)
This service starts the processing of a schedule table at “Offset” relative to the “Now” value on the underlying counter.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ScheduleTableID |
ScheduleTable Identifier |
[in] |
Offset |
The clock value from the current time to the start of the schedule (the tick value of the counter corresponds to the schedule) |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No errors |
E_OS_ID |
ScheduleTableID is invalid |
E_OS_VALUE |
Offset is greater than (OsCounterMaxAllowedValue-InitialOffset) or equal to 0 |
E_OS_STATE |
schedule has started |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
Application state error / No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
Waiting the execution result timeout. |
Example
Counter_0: MaxTick:1000, MinTick:1, CounterType: SOFTWARE
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
OsScheduleTable_0: Counter:Counter_0
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ScheduleTableStatusType ststatus;
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/* default : ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_STOPPED */
StartScheduleTableRel(OsScheduleTable_0, 2);
/* OsScheduleTable_0 is in queue but not started. */
/* ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_STOPPED */
IncrementCounter(Counter_0);
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/* ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_RUNNING */
......
}
StartScheduleTableAbs¶
StatusType StartScheduleTableAbs(ScheduleTableType ScheduleTableID, TickType Start)
This service starts the processing of a schedule table at an absolute value “Start” on the underlying counter.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ScheduleTableID |
ScheduleTable Identifier |
[in] |
Start |
The clock value at which the schedule starts processing (the absolute tick value of the counter corresponding to the schedule) |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No errors |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid ScheduleTableID |
E_OS_VALUE |
Start is greater than OsCounterMaxAllowedValue |
E_OS_STATE |
schedule has started |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
Waiting the execution result timeout. |
StopScheduleTable¶
StatusType StopScheduleTable(ScheduleTableType ScheduleTableID)
This service cancels the processing of a schedule table immediately at any point while the schedule table is running.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ScheduleTableID |
ScheduleTable Identifier |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No errors |
E_OS_ID |
ScheduleTableID is invalid |
E_OS_NOFUNC |
The schedule has stopped |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
Waiting the execution result timeout. |
Example
Example.1
Counter_0: MaxTick:1000, MinTick:1, CounterType: SOFTWARE
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
OsScheduleTable_0: Counter:Counter_0
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ScheduleTableStatusType ststatus;
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/* default : ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_STOPPED */
StartScheduleTableRel(OsScheduleTable_0, 1);
/* OsScheduleTable_0 is in queue but not started. */
/* ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_STOPPED */
IncrementCounter(Counter_0);
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/* ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_RUNNING */
StopScheduleTable(OsScheduleTable_0);
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/* ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_STOPPED */
......
}
NextScheduleTable¶
StatusType NextScheduleTable(ScheduleTableType ScheduleTableID_From, ScheduleTableType ScheduleTableID_To)
This service switches the processing from one schedule table to another schedule table.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ScheduleTableID_From |
Schedules currently being processed |
[in] |
ScheduleTableID_To |
Next processing schedule with a series of trigger points |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No errors |
E_OS_ID |
ScheduleTableID_From or ScheduleTableID_To is invalid |
E_OS_NOFUNC |
ScheduleTableID_From did not start |
E_OS_STATE |
ScheduleTableID_To has started or is in Next |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
These two schedule tables do not belong to the same core |
Example
Counter_0: MaxTick:1000, MinTick:1, CounterType: SOFTWARE
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
OsScheduleTable_0: Counter:Counter_0,
The Final ExpiryPoint: ExpPoint Offset: [n]
OsScheduleTable_1: Counter:Counter_0
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ScheduleTableStatusType ststatus;
StartScheduleTableRel(OsScheduleTable_0, 1);
IncrementCounter(Counter_0);
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/* ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_RUNNING */
NextScheduleTable(OsScheduleTable_0, OsScheduleTable_1);
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_1, &ststatus);
/* ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_NEXT */
IncrementCounter(Counter_0); /* Execult [n] times.*/
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/* ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_STOPPED */
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_1, &ststatus);
/* ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_RUNNING */
......
}
StartScheduleTableSynchron¶
StatusType StartScheduleTableSynchron(ScheduleTableType ScheduleTableID)
This service starts an explicitly synchronized schedule table synchronously.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ScheduleTableID |
ScheduleTable Identifier |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No errors |
E_OS_ID |
ScheduleTableID is invalid |
E_OS_STATE |
ScheduleTableID has been started |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The object is not belong to local core |
Example
Example.1
Counter_0: MaxTick:1000, MinTick:1, CounterType: SOFTWARE
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
OsScheduleTable_0: Counter:Counter_0, Sync Strategy:EXPLICIT
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ScheduleTableStatusType ststatus;
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/* default : ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_STOPPED */
StartScheduleTableSynchron(OsScheduleTable_0);
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/* default : ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_WAITING */
......
}
Note
仅在SC3、SC4下有效
This is valid only under SC3 and SC4.
调度表同步策略必须是显性。
The schedule table synchronization strategy must be explicit.
SyncScheduleTable¶
StatusType SyncScheduleTable(ScheduleTableType ScheduleTableID, TickType value)
This service provides the schedule table with a synchronization count and start synchronization.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ScheduleTableID |
ScheduleTable Identifier |
value |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No errors |
E_OS_ID |
ScheduleTableID is invalid or the schedule cannot be synchronized (OsScheduleTblSyncStrategy is not set or OsScheduleTblSynStrategy = IMPLICIT) |
E_OS_VALUE |
Value is out of range |
E_OS_STATE |
The status of ScheduleTableID is SCHEDULETABLE_STOPPED |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_CORE |
The object is not belong to local core |
Example
Counter_0: MaxTick:1000, MinTick:1, CounterType: SOFTWARE
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
OsScheduleTable_0: Counter:Counter_0, Sync Strategy:EXPLICIT
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ScheduleTableStatusType ststatus;
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/* default : ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_STOPPED */
StartScheduleTableSynchron(OsScheduleTable_0);
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/* default : ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_WAITING */
SyncScheduleTable(OsScheduleTable_0, 1);
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/*default : ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_RUNNING_AND_SYNCHRONOUS*/
......
}
Note
仅在SC3、SC4下有效
It is valid only under SC3 and SC4.
调度表同步策略必须是显性
The schedule table synchronization strategy must be explicit.
SetScheduleTableAsync¶
StatusType SetScheduleTableAsync(ScheduleTableType ScheduleTableID)
Stop schedule table explicit sync and set state to running.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ScheduleTableID |
ScheduleTable Identifier |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid ScheduleTableID |
E_OS_STATE |
The schedule table is not running |
E_OS_CORE |
The object is not belong to local core |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
Example
Counter_0: MaxTick:1000, MinTick:1, CounterType: SOFTWARE
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
OsScheduleTable_0: Counter:Counter_0, Sync Strategy:EXPLICIT
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ScheduleTableStatusType ststatus;
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/* default : ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_STOPPED */
StartScheduleTableSynchron(OsScheduleTable_0);
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/* default : ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_WAITING */
SyncScheduleTable(OsScheduleTable_0, 1);
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/*default : ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_RUNNING_AND_SYNCHRONOUS*/
SetScheduleTableAsync(OsScheduleTable_0);
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &ststatus);
/*default : ststatus = SCHEDULETABLE_RUNNING */
......
}
Note
仅在SC3、SC4下有效
It is valid only under SC3 and SC4.
调度表同步策略必须是显性
The schedule table synchronization strategy must be explicit.
GetScheduleTableStatus¶
StatusType GetScheduleTableStatus(ScheduleTableType ScheduleTableID, ScheduleTableStatusRefType ScheduleStatus)
Get the status of the specified schedule.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ScheduleTableID |
ScheduleTable Identifier |
[out] |
ScheduleStatus |
Pointer to the status value of the obtained schedule |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid ScheduleTableID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal, or rpcData is NULL_PTR. |
E_OS_CORE |
The remote core is not running |
E_OS_VALUE |
Parameter address is invalid |
E_BUSY |
The free node can’t be gotten from free queue. |
E_OS_TIMEOUT |
Waiting the execution result timeout. |
Hook(Functions)¶
ORIENTAIS OS为用户提供了一系列钩子函数功能(Hook)。例如在钩子函数StartupHook中初始化一些硬件,在钩子函数ErrorHook中捕获并处理的一些错误。
ORIENTAIS OS provides users with a series of hook functions. For example, hardware can be initialized in the StartupHook function, and errors can be captured and handled in the ErrorHook function.
ErrorHook¶
void ErrorHook(StatusType Error)
The specific error hook is called whenever a Task or ISR calls system service to cause an error.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Error |
Error code |
- Return type
void
Example
TASK(TaskInit)
{
StatusType ret;
ret = ActivateTask(OS_TASK_INVALID); /* step 1 */
/* step 3 : ret = E_OS_ID */
......
}
void ErrorHook(StatusType Error)
{
/* step 2 */
if (E_OS_ID == Error)
{
......
}
}
Note
执行错误处理。该接口由用户实现错误处理,并由ORIENTAIS OS调用。
Performs error handling. This interface is implemented by the user for error handling and is called by ORIENTAIS OS.
用户可以通过输入参数<Error>的值来了解错误类型。
Users can determine the error type from the value of the input parameter <Error>.
PostTaskHook¶
void PostTaskHook(void)
This hook routine is called by ORIENTAIS OS after executing the current task, but before leaving the task’s running state (to allow evaluation of the TaskID by GetTaskID).
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
void
Example
TASK(TaskInit)
{
TerminateTask(); /* step 1 */
/* TerminateTask, ChainTask, WaitEvent and Schedule can make OS scheduling.*/
/* If a task is terminated, the PostTaskHook shall be triggered.*/
......
}
void PostTaskHook ()
{
TaskType taskid;
/* step 2 */
GetTaskID(&taskid);
/* taskid = OS_TASK_INVALID */
......
}
Note
该接口由用户实现,并由ORIENTAIS OS调用。
This interface is implemented by the user and is called by ORIENTAIS OS.
PreTaskHook¶
void PreTaskHook(void)
This hook routine is called by ORIENTAIS OS before executing a new task, but after the transition of the task to the running state (to allow evaluation of the TaskID by GetTaskID.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
void
Example
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ActivateTask(Task0); /* step 1 */
/* Before a task execult, the PreTaskHook shall be triggered.*/
......
}
TASK(Task0)
{
TaskType taskid;
/* step 3 */
GetTaskID(&taskid);
/* taskid = Task0 */
}
void PreTaskHook()
{
/* step 2 */
......
}
Note
该接口由用户实现,并由ORIENTAIS OS调用。
This interface is implemented by the user and is called by ORIENTAIS OS.
StartupHook¶
void StartupHook(void)
This hook routine is called by the operating system at the end of the operating system in itialisation and before the scheduler is running. At this time the applicationcan initialise device drivers etc.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
void
Example
void main()
{
......
StartOS(OSDEFAULTAPPMODE); /*step 1*/
/*step 3*/
......
}
void StartupHook()
{
/*step 2*/
......
}
Note
该接口由用户实现,并由ORIENTAIS OS调用。
This interface is implemented by the user and is called by ORIENTAIS OS.
ShutdownHook¶
void ShutdownHook(StatusType Error)
This hook routine is called by the operating system when the OS service ShutdownOS has been called. This routine is called during the operating system shutdown.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Error |
Error code |
- Return type
void
Example
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ShutdownOS(E_OK); /*step 1*/
/* Won't execute here.*/
/* If user calls ShutdownAllCores in mutil-core, a similar situation shall happen in every core. */
......
}
void ShutdownHook()
{
/*step 2*/
......
}
Note
该接口由用户实现,并由ORIENTAIS OS调用。
This interface is implemented by the user and is called by ORIENTAIS OS.
ProtectionHook¶
ProtectionReturnType ProtectionHook(StatusType Fatalerror)
This hook routine is called by the operating system when the OS service protection functions.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Fatalerror |
Error code |
- Return type
ProtectionReturnType
Example
App0: Non-Trusted
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
TimingProtection: ExecutionBudget:0.005
uint8 var;
TASK(TaskInit)
{
GetSpinlock(Spinlock_0);
TerminateTask(); /* step 1 : Invalid Calling, It triggers E_OS_SPINLOCK error.*/
var = 0; /* Writing global variable to trigger the memory protection*/
DelayMs(5); /* Execution time out to trigger the timing protection*/
}
ProtectionReturnType ProtectionHook(StatusType Fatalerror)
{
/*step 2*/
ProtectionReturnType ret = PRO_IGNORE;
if (E_OS_SPINLOCK == Fatalerror)
{
ret = PRO_TERMINATETASKISR;
/*Return with PRO_TERMINATETASKISR.
The fault task/isr shall be terminated.*/
}
else if (E_OS_PROTECTION_MEMORY == Fatalerror)
{
ret = PRO_SHUTDOWN;
/*Return with PRO_SHUTDOWN.
The OS shall shutdown.*/
}
else if (E_OS_PROTECTION_TIME == Fatalerror)
{
ret = PRO_TERMINATEAPPL_RESTART;
/*Return with PRO_TERMINATEAPPL_RESTART.
The fault application shall restart.*/
}
......
}
Note
该接口由用户实现错误处理,并由ORIENTAIS OS调用。
This interface is implemented by the user for error handling and is called by ORIENTAIS OS.
用户可以通过返回值来选择五种处理方式中的一种处理。
Users can select one of five processing methods through the return value.
IdleHook_Core<n>¶
void IdleHook_Core<n>(void)
This HOOK is called when ORIENTAIS OS enters an idle task.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
void
Note
该接口由用户实现,并由ORIENTAIS OS调用。
This interface is implemented by the user and is called by ORIENTAIS OS.
如果没有正在运行的任务/中断,则调用此接口。
This interface is called when no task or interrupt is running.
ErrorHook_<ApplicationName>¶
void ErrorHook_<ApplicationName> (StatusType Error)
This HOOK is called when ORIENTAIS OS enters an idle task.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Error |
Error code |
- Return type
void
Note
该接口由用户实现,并由ORIENTAIS OS调用。
This interface is implemented by the user and is called by ORIENTAIS OS.
StartupHook_<ApplicationName>¶
void StartupHook_<ApplicationName> (void)
When a specific application has the startup hook function enabled, ORIENTAIS OS calls this function when that application starts.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
void
Note
该接口由用户实现,并由ORIENTAIS OS调用。
This interface is implemented by the user and is called by ORIENTAIS OS.
ShutdownHook_<ApplicationName>¶
void ShutdownHook_<ApplicationName> (StatusType Fatalerror)
When a specific application has the shutdown hook function enabled, ORIENTAIS OS calls this hook function when that application is being shut down.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Fatalerror |
Error code |
- Return type
void
Note
该接口由用户实现,并由ORIENTAIS OS调用。
This interface is implemented by the user and is called by ORIENTAIS OS.
OS-APP(Functions)¶
Os能够支持一系列操作系统对象的集合(任务,中断,Alarm,调度表,计数器)。该对象集合称为OS-Application。
The OS can support a collection of operating system objects (tasks, interrupts, alarms, schedule tables, counters). This object collection is called an OS-Application.
存在两类OS-Application:
There are two types of OS-Applications:
可信OS-Application在监视或保护功能关闭的情况下运行。他们能够无限制地访问内存,操作系统模块的API,并且不需要在运行时受到强制时间限制。当处理器支持的情况下,允许它们在特权模式下运行。
Trusted OS-Applications run with monitoring or protection functions disabled. They have unrestricted access to memory and OS module APIs, and are not subject to mandatory time constraints during runtime. When processor support is available, they are permitted to run in privileged mode.
不可信任的OS-Application在监视或保护功能开启的情况下运行。它们对内存的访问受到限制,对操作系统模块的API的访问受到限制,并且需要在运行时进行强制时间限制。当处理器支持时,不允许它们在特权模式下运行。
Untrusted OS-Applications run with monitoring or protection functions enabled. Their access to memory is restricted, access to OS module APIs is limited, and they are subject to mandatory time constraints during runtime. When processor support is available, they are not permitted to run in privileged mode.
ORIENTAIS OS提供一些服务,这些服务向调用者提供有关访问权限和对象成员身份的信息。这些服务主要在OS-Application之间检查访问权限和参数的情况下使用。
ORIENTAIS OS provides services that supply callers with information about access rights and object membership. These services are primarily used to check access rights and parameters between OS-Applications.
OS-Applications的状态决定其操作系统对象从其他OS-Applications访问的范围。每个OS-Application始终处于以下状态之一:
The state of an OS-Application determines the accessibility scope of its operating system objects from other OS-Applications. Each OS-Application is always in one of the following states:
激活且可访问的(APPLICATION_ACCESSIBLE):可以从其他OS-Applications访问操作系统对象。这是启动时的默认状态。
Active and accessible (APPLICATION_ACCESSIBLE): Operating system objects can be accessed from other OS-Applications. This is the default state at startup.
当前处于重启阶段(APPLICATION_RESTART)。无法从其他OS-Applications访问操作系统对象。状态有效,直到OS-Application调用AllowAccess。
Currently in restart phase (APPLICATION_RESTART): Operating system objects cannot be accessed from other OS-Applications. This state remains valid until the OS-Application calls AllowAccess.
已终止且不可访问(APPLICATION_TERMINATED):不能从其他OS-Applications访问操作系统对象。状态不会改变。
Terminated and inaccessible (APPLICATION_TERMINATED): Operating system objects cannot be accessed from other OS-Applications. This state does not change.
Figure显示了状态的转换:
The figure shows the state transitions:
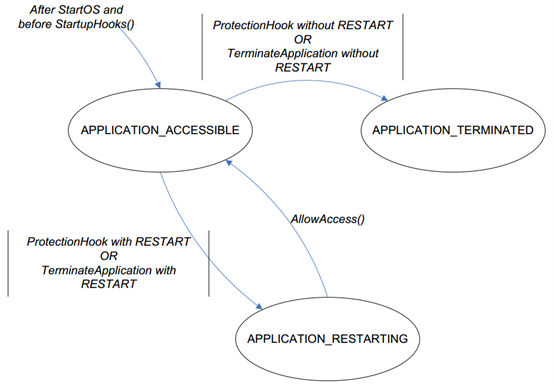
OS-Applications状态图 (OS-Application State Diagram)¶
GetApplicationID¶
ApplicationType GetApplicationID(void)
Get the OS-Application ID of the object calling the API.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
ApplicationType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
Application |
number |
INVALID_OSAPPLICATION |
INVALID OSAPPLICATION Id |
Note
在SC3、SC4下有效
Valid under SC3 and SC4.
GetCurrentApplicationID¶
ApplicationType GetCurrentApplicationID(void)
Get the OS-Application ID to which the currently running Task/ISR/Hook belongs.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
ApplicationType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
Application |
number |
INVALID_OSAPPLICATION |
INVALID OSAPPLICATION Id |
Example
App0:
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
App1: Trusted
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL
TrustedFunction:
TRUSTED_OsApplicationTrustedFunction_0
TASK(TaskInit)
{
uint8 para = 0;
/* step 1*/
ApplicationType application;
application = GetApplicationID();
/* application = App0*/
application = GetCurrentApplicationID();
/* application = App0*/
ret= CallTrustedFunction(CFG_TRUSTED_OsApplicationTrustedFunction_0_IX, ¶)
/* step 3 ret = E_OK*/
}
void TRUSTED_OsApplicationTrustedFunction_0(TrustedFunctionIndexType ix,
TrustedFunctionParameterRefType ref)
{
/* step 2*/
ApplicationType application;
application = GetApplicationID();
/* application = App1*/
application = GetCurrentApplicationID();
/* application = App0*/
......
}
Note
GetApplicationID和GetCurrentApplicationID区别在于GetApplicationID可以获取可信函数的应用程序ID。
The difference between GetApplicationID and GetCurrentApplicationID is that GetApplicationID can retrieve the application ID of a trusted function.
在SC3、SC4下有效
Valid under SC3 and SC4
CheckObjectAccess¶
ObjectAccessType CheckObjectAccess(ApplicationType ApplID, ObjectTypeType ObjectType, AppObjectId ObjectID)
This service determines if the OS-Applications, given by ApplID, is allowed to use the IDs of a Task, ISR, Resource,Counter, Alarm or Schedule Table in API calls.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ApplID |
OsApplication number |
[in] |
ObjectType |
Entity type, see |
[in] |
ObjectID |
Entity number |
- Return type
ObjectAccessType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
ACCESS |
the ApplID has access to the object. |
NO_ACCESS |
the ApplID is invalid; ObjectType is invalid;the ApplID does not have access to the object. |
Example
App0:
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
App1:
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ObjectAccessType objectaccess;
objectaccess = CheckObjectAccess(App0, OBJECT_TASK, TaskInit);
/* objectaccess = ACCESS */
objectaccess = CheckObjectAccess(App0, OBJECT_TASK, Task0);
/* objectaccess = NO_ACCESS*/
}
Note
请确保对象类型和对象ID是匹配的。
Ensure that the object type and object ID match.
在SC3,SC4下有效
Valid under SC3 and SC4
CheckObjectOwnership¶
ApplicationType CheckObjectOwnership(ObjectTypeType ObjectType, AppObjectId ObjectID)
This service determines to which OS-Application a given Task, ISR, Resource, Counter, Alarm or Schedule Table belongs.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ObjectType |
Entity type, see |
[in] |
ObjectID |
Entity number |
- Return type
ApplicationType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
the OS-Application to which the object ObjectType belongs. |
|
INVALID_OSAPPLICATION |
the ObjectID does not exist; ObjectType is invalid; the object type is BJECT_RESOURCE and the object is RES_SCHEDULER. |
Example
App0:
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
App1:
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ApplicationType application;
application = CheckObjectOwnership(OBJECT_TASK, TaskInit);
/* objectaccess = App0,*/
application = CheckObjectOwnership(OBJECT_TASK, Task0);
/* objectaccess = App1*/
}
Note
请确保对象类型和对象ID是匹配的。
Ensure that the object type and object ID match.
在SC3,SC4下有效
Valid under SC3 and SC4
TerminateApplication¶
StatusType TerminateApplication(ApplicationType Application, RestartType RestartOption)
This service returns the current state of an OS-Application.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Application |
Application user want to end |
[in] |
RestartOption |
RESTART: Perform a restart NO_RESTART: Do not restart the app |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No errors |
E_OS_ID |
<Application> was not valid (only in EXTENDED status) |
E_OS_VALUE |
<RestartOption> was neither RESTART nor NO_RESTART (only in EXTENDED status) |
E_OS_ACCESS |
The caller does not have the right to terminate<Application> (only in EXTENDED status) |
E_OS_STATE |
The state of <Application> does not allow terminating <Application> |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Call level at wrong context. |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Interrupts are disabled/suspended, OS shall ignore the service. |
Example
Example.1
Counter_0: MaxTick:1000, MinTick:1, CounterType:SOFTWARE
App0:
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
App1:
Task0:Priority:2,PreemptivePolicy:FULL,Resource:Resource_0, AccessingApplication: App0
Alarm:Alarm_0, Couner:Counter_0,
AccessingApplication: App0
ScheduleTable:OsScheduleTable_0, Couner:Counter_0,
AccessingApplication: App0
TASK(TaskInit)
{
StatusType ret;
TickType tick;
TaskStateRefType taskState;
ScheduleTableStatusType scheduletableStatus;
ApplicationStateType applicationState;
GetApplicationState(App1, &applicationState);
/* applicationState = APPLICATION_ACCESSIBLE */
SetRelAlarm(Alarm_0,1,0);
StartScheduleTableRel(OsScheduleTable_0, 1);
IncrementCounter(Counter_0);
ret = GetAlarm(Alarm_0, &tick);
/* ret = E_OK*/
ret = GetTaskState(Task0, &taskState);
/* taskState = TASK_STATE_WAITING */
GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &scheduletableStatus);
/* scheduletableStatus = SCHEDULETABLE_RUNNING */
ActivateTask(Task0);/* Activating Task0 to terminate App1*/
applicationState = APPLICATION_ACCESSIBLE;
while(applicationState == APPLICATION_ACCESSIBLE)
{
GetApplicationState(App1, &applicationState);
}
ret = GetAlarm(Alarm, &tick);
/* ret = E_OS_ACCESS*/
ret = GetTaskState(OsTask_0, &taskState);
/* ret = E_OS_ACCESS*/
ret = GetScheduleTableStatus(OsScheduleTable_0, &scheduletableStatus);
/* ret = E_OS_ACCESS*/
GetApplicationState(App1, &applicationState);
/* applicationState = APPLICATION_TERMINATED */
}
TASK(Task0)
{
TerminateApplication(App1, NO_RESTART);
}
Example.2
App0:
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
App1:
RestartTask: Task_Restart
Task0:Priority:2,PreemptivePolicy:FULL,
AccessingApplication: App0
Task_Restart: Priority:3,PreemptivePolicy:FULL
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ApplicationStateType applicationState;
/* step 1*/
GetApplicationState(App1, &applicationState);
/* applicationState = APPLICATION_ACCESSIBLE */
ActivateTask(Task0);
while(applicationState == APPLICATION_ACCESSIBLE)
{
GetApplicationState(App1, &applicationState);
}
/* step 4*/
GetApplicationState(App1, &applicationState);
/* applicationState = APPLICATION_RESTARTING */
}
TASK(Task0)
{
/* step 2*/
TerminateApplication(App1, RESTART);
}
TASK(Task_Restart)
{
/* step 3*/
}
Note
如果重新启动的OS-Application配置了重启任务,则该任务将在重新启动时被激活。
If the OS-Application to be restarted is configured with a restart task, that task is activated during the restart.
在SC3,SC4下有效
Valid under SC3 and SC4
AllowAccess¶
StatusType AllowAccess(void)
This service sets the own state of an OS-Application from APPLICATION_RESTARTING to APPLICATION_ACCESSIBLE.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No errors |
E_OS_STATE |
The OS-Application of the caller is in the wrong state |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Call level at wrong context. |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Interrupts are disabled/suspended, OS shall ignore the service. |
Example
Example.1
App0:
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
App1:
RestartTask: Task_Restart
Task0:Priority:2,PreemptivePolicy:FULL,
AccessingApplication: App0
Task_Restart: Priority:3,PreemptivePolicy:FULL
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ApplicationStateType applicationState;
/* step 1*/
GetApplicationState(App1, &applicationState);
/* applicationState = APPLICATION_ACCESSIBLE */
ActivateTask(Task0);
while(applicationState == APPLICATION_ACCESSIBLE)
{
GetApplicationState(App1, &applicationState);
}
while(applicationState != APPLICATION_ACCESSIBLE)
{
GetApplicationState(App1, &applicationState);
}
/* step 4*/
GetApplicationState(App1, &applicationState);
/* applicationState = APPLICATION_ACCESSIBLE */
}
TASK(Task0)
{
/* step 2*/
TerminateApplication(App1, RESTART);
}
TASK(Task_Restart)
{
/* step 3*/
AllowAccess();
}
Note
在SC3,SC4下有效
Valid under SC3 and SC4
GetApplicationState¶
StatusType GetApplicationState(ApplicationType Application, ApplicationStateRefType Value)
This service returns the current state of an OS-Application.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Application |
Application number user want to get |
[out] |
Value |
ACCESSIBLE:accessible RESTARTING:Restarting TERMINATED:ended |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No errors |
E_OS_ID |
<Application> is not valid. |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Call level at wrong context. |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Interrupts are disabled/suspended, OS shall ignore the service. |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
The address of Value is invalid. |
Note
在SC3,SC4下有效
Valid under SC3 and SC4
Memory(Protection Functions)¶
内存保护策略是基于可执行程序的(数据,代码和堆栈)段。
The memory protection strategy is based on the segments (data, code, and stack) of the executable program.
堆栈:OS-Application包含许多任务和中断。根据定义,这些对象的堆栈仅属于所有者,因此即使这些对象属于同一OS-Application,对象之间也不应共享堆栈数据。
Stack: An OS-Application contains multiple tasks and interrupts. By definition, the stacks of these objects belong exclusively to their owners; therefore, stack data should not be shared between objects, even if they belong to the same OS-Application.
任务和中断堆栈的内存保护非常有用,主要有两个原因:
Memory protection for task and interrupt stacks is highly beneficial for two main reasons:
与堆栈监视相比,可以更直接地检测任务或中断的堆栈上溢和下溢
It enables more direct detection of stack overflow and underflow for tasks or interrupts compared to stack monitoring.
在OS-Application的组成部分之间提供保护,例如满足一些安全约束
It provides protection between components of an OS-Application, such as fulfilling certain security constraints.
数据:OS-Application具有私有数据段,而任务/中断具有私有数据段。OS-Application的所有任务/中断共享OS-Application的私有数据段。
Data: An OS-Application has a private data segment, and tasks/interrupts have their own private data segments. All tasks/interrupts within an OS-Application share the OS-Application’s private data segment.
代码:代码段是OS-Application专用的,也可以在所有OS-Applications之间共享(以使用共享库)。在不使用代码保护的情况下,执行不正确的代码最终将导致内存,时序或服务冲突。
Code: Code segments are dedicated to an OS-Application but can also be shared among all OS-Applications (e.g., for using shared libraries). Without code protection, executing incorrect code will eventually result in memory, timing, or service conflicts.
CheckISRMemoryAccess¶
AccessType CheckISRMemoryAccess(ISRType ISRID, MemoryStartAddressType Address, MemorySizeType Size)
This service checks if a memory region is write/read/execute accessible and also returns information if the memory region is part of the stack space.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
ISRID |
Interrupt Identifier |
[in] |
Address |
Memory area start address |
[in] |
Size |
Memory area size |
- Return type
AccessType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
NO_PERMISSION |
Permission denied |
OSMEMORY_IS_READABLE(Access) |
Non-zero means read permission |
OSMEMORY_IS_WRITEABLE(Access) |
Non-zero means write permission |
OSMEMORY_IS_EXECUTABLE(Access) |
Non-zero means execute permission |
OSMEMORY_IS_STACKSPACE(Access) |
Non-zero means stack space |
Note
在SC3,SC4下有效
Valid under SC3 and SC4
请在可信OS-Application的任务或中断中调用该服务
Call this service from within a task or interrupt of a trusted OS-Application.
CheckTaskMemoryAccess¶
AccessType CheckTaskMemoryAccess(TaskType TaskID, MemoryStartAddressType Address, MemorySizeType Size)
This service checks if a memory region is write/read/execute accessible and also returns information if the memory region is part of the stack space.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
TaskID |
Task Identifier |
[in] |
Address |
Memory area start address |
[in] |
Size |
Memory area size |
- Return type
AccessType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
NO_PERMISSION |
Permission denied |
OSMEMORY_IS_READABLE(Access) |
Non-zero means read permission |
OSMEMORY_IS_WRITEABLE(Access) |
Non-zero means write permission |
OSMEMORY_IS_EXECUTABLE(Access) |
Non-zero means execute permission |
OSMEMORY_IS_STACKSPACE(Access) |
Non-zero means stack space |
Example
App0: Trusted
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
App1: No Trusted
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL
ERAY_INT0: Priority:101, Category: CATEGORY_2
#define OS_START_SEC_CORE0_APP0_PRI_DATA
#include “Os_Mp_MemMap.h”
uint8 app0Data;
#define OS_STOP_SEC_CORE0_APP0_PRI_DATA
#include “Os_Mp_MemMap.h”
#define OS_START_SEC_CORE0_APP1_PRI_DATA
#include “Os_Mp_MemMap.h”
uint8 app1Data;
#define OS_STOP_SEC_CORE0_APP1_PRI_DATA
#include “Os_Mp_MemMap.h”
TASK(TaskInit)
{
AccessType access;
access = CheckTaskMemoryAccess(Task0, &app1Data, 1);
/* access = 3 ( 0011 ) 4:execult | 2:write | 1:read */
access = CheckISRMemoryAccess(CFG_ISR_ERAY_INT0_ID, &app1Data, 1);
/* access = 3 ( 0011 )*/
access = CheckTaskMemoryAccess(Task0, &app0Data, 1);
/* access = 0*/
access = CheckISRMemoryAccess(CFG_ISR_ERAY_INT0_ID, &app0Data, 1);
/* access = 0*/
}
Note
在SC3,SC4下有效
Valid under SC3 and SC4
请在可信OS-Application的任务或中断中调用该服务
Call this service from within a task or interrupt of a trusted OS-Application.
Service(Protection Functions)¶
当OS-Application进行API调用,服务保护需要考虑多种情况:
When an OS-Application makes an API call, service protection must consider various scenarios:
句柄无效或超出范围
The handle is invalid or out of range.
在错误的调用场景中,例如在StartupHook中调用ActivateTask()
In an incorrect calling context, such as calling ActivateTask() within StartupHook.
或未能进行API调用导致ORIENTAIS OS处于未定义状态,例如:在占用资源期间结束任务
Or failure to make proper API calls resulting in ORIENTAIS OS entering an undefined state, for example: terminating a task while holding resources.
会影响系统中其他所有OS-Application的行为,例如:ShutdownOS()
Affecting the behavior of all other OS-Applications in the system, such as: ShutdownOS().
操纵属于另一个OS-Application的操作系统对象(该OS对象没有必需的权限),例如 OS-Application尝试对其不拥有访问权限的任务执行ActivateTask()
Manipulating operating system objects belonging to another OS-Application (without the required permissions), for example, an OS-Application attempting to execute ActivateTask() on a task it lacks access permissions for.
关于系统服务在错误的场景中被调用,请参阅**错误!未找到引用源**。
For system services called in incorrect contexts, refer to Error! Reference source not found.
CallTrustedFunction¶
StatusType CallTrustedFunction(TrustedFunctionIndexType FunctionIndex, TrustedFunctionParameterRefType FunctionParams)
The interface provided by trusted functions to external calls. Untrusted apps can access internal resources of trusted apps.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
FunctionIndex |
The index number of the trusted function |
[in] |
FunctionParams |
Pointer to a trusted function parameter |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal |
E_OS_SERVICEID |
Incoming trusted function index error |
E_OS_CORE |
The object is not belong to local core |
Example
App0:
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
App1: Trusted
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL
TrustedFunction:
TRUSTED_OsApplicationTrustedFunction_0
TASK(TaskInit)
{
/* step 1*/
ret= CallTrustedFunction(CFG_TRUSTED_OsApplicationTrustedFunction_0_IX);
/* step 3 ret = E_OK*/
}
void TRUSTED_OsApplicationTrustedFunction_0(TrustedFunctionIndexType ix,
TrustedFunctionParameterRefType ref)
{
/* step 2*/
......
}
Note
在SC3,SC4下有效
Valid under SC3 and SC4
System(Control Functions)¶
StartOS¶
void StartOS(AppModeType Mode)
The user can call this system service to start the operating system in a specific mode.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Mode |
Application mode (launch mode), defined by the user on the tool |
- Return type
void
Note
系统初始化时必须使用此接口。
This interface must be used during system initialization.
所有核必须以相同模式启动。
All cores must boot in the same mode.
ShutdownOS¶
void ShutdownOS(StatusType Error)
The user can call this system service to abort the overall system (e.g. emergency off).
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Error |
Error type, see StatusType for detail |
- Return type
void
Note
该服务调用者所属OS-Application必须是可信OS-Application
The OS-Application to which the service caller belongs must be a trusted OS-Application.
GetActiveApplicationMode¶
AppModeType GetActiveApplicationMode(void)
This service returns t he current application mode. It may be used to write mode dependent code.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
AppModeType
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
void mian()
{
......
StartOS(OSDEFAULTAPPMODE);
......
}
TASK(TaskInit)
{
AppModeType appMode;
appMode = GetActiveApplicationMode();
/* appMode = OSDEFAULTAPPMODE */
}
Multi-Core(Functions)¶
GetCoreID¶
CoreIdType GetCoreID(void)
Get the logical ID of the currently executing core.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
CoreIdType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
Logic |
ID |
OS_CORE_INVALID |
INVALID CORE ID |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
void main(void)
{
CoreIdType coreId;
coreId = GetCoreID();
......
}
Note
用户可以在StratOS之前调用该服务
Users can call this service before StartOS.
GetNumberOfActivatedCores¶
uint32 GetNumberOfActivatedCores(void)
Get the number of cores currently activated (cores managed by ORIENTAIS OS)
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
uint32
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
The |
number of cores currently activated |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
void main(void)
{
uint32 coreNum;
coreNum = GetNumberOfActivatedCores ();
......
}
StartCore¶
void StartCore(CoreIdType CoreID, StatusType *Status)
Start the specified Autosar core.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
CoreID |
||
[out] |
Status |
StatusType, The return value of this service |
- Return type
void
Example
void main ()
{
StatusType rv;
switch (GetCoreID())
{
case OS_CORE_ID_MASTER:
/* Check the CPU Information */
/* Software and hardware initial. */
/* The master core starts automatically. */
StartOS(OSDEFAULTAPPMODE);
/* If other cores exist, they can be started by calling StartCore*/
#if(TRUE == CFG_CORE1_AUTOSAROS_ENABLE)
StartCore(OS_CORE_ID_1, &rv);
#endif
......
break;
case OS_CORE_ID_1:
......
/* The slave core is started by master core. */
StartOS(OSDEFAULTAPPMODE);
......
break;
......
}
......
}
StartNonAutosarCore¶
void StartNonAutosarCore(CoreIdType CoreID, StatusType *Status)
Start the specified non-Autosar core.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
CoreID |
||
[out] |
Status |
StatusType, The return value of this service |
- Return type
void
Example
Cores Number:1
#define CFG_CORE_MAX 3U
#define OS_CORE_ID_MASTER ((Os_CoreIdType)0U)
#define OS_CORE_ID_0 ((Os_CoreIdType)0U)
#define OS_NONAUTOSARCORE_ID_0 ((Os_CoreIdType)1U)
#define OS_NONAUTOSARCORE_ID_1 ((Os_CoreIdType)2U)
void main()
{
......
StartNonAutosarCore(OS_NONAUTOSARCORE_ID_0);
......
StartNonAutosarCore(OS_NONAUTOSARCORE_ID_1);
......
}
Note
该函数仅允许启动非Autosar内核。
This function permits starting only non-AUTOSAR kernels.
ShutdownAllCores¶
void ShutdownAllCores(StatusType Error)
Get the logical ID of the currently executing core.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Error |
error code, see StatusType |
- Return type
void
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
Logic |
ID |
OS_CORE_INVALID |
Example
App0: Trusted
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
TASK(TaskInit)
{
ShutdownAllCores(E_OK);
}
void ShutdownHook(StatusType Error)
{
/* All cores shall enter the hook, and the Error is E_OK */
}
Note
该服务调用者所属OS-Application必须是可信OS-Application。
The calling OS-Application of this service must be a trusted OS-Application.
ControlIdle¶
StatusType ControlIdle(CoreIdType CoreID, IdleModeType IdleMode)
This API allows the caller to select the idle mode action which is performed during idle time of the OS.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
CoreID |
Core Identifier |
[in] |
IdleMode |
Selected Idle Mode |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid core and/or invalid idleMode |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Call at interrupt level |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Interrupts are disabled/suspended, OS shall ignore the service |
Example
App0: Trusted
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
void main (void)
{
StatusType ret;
ret = ControlIdle(OS_CORE_ID_0, OS_RUN);
}
Spinlock(Functions)¶
在多核中,需要一种新的机制来支持不同核上任务的互斥。这种新机制不适用于同核上的任务,且将返回错误。
In multi-core systems, a new mechanism is required to support mutual exclusion among tasks on different cores. This new mechanism is not applicable to tasks on the same core and returns an error.
“SpinlockType”是类似于”ResourceType”,且离线配置的自旋锁。
“SpinlockType” is a spinlock similar to “ResourceType” and is configured offline.
自旋锁是一种繁忙的等待机制,它轮询某个自旋锁变量(Spinlock Variable)直到可用。
A spinlock is a busy-waiting mechanism that polls a spinlock variable until it becomes available.
一旦自旋锁被任务或2类中断占用,其他内核上的任务或2类中断将无法占用这个自旋锁。自旋锁机制不会在轮询锁定变量时对其他任务进行调度。
Once a spinlock is acquired by a task or a Category 2 interrupt, tasks or Category 2 interrupts on other cores cannot acquire this spinlock. The spinlock mechanism does not schedule other tasks while polling the lock variable.
GetSpinlock¶
StatusType GetSpinlock(SpinlockIdType SpinlockId)
GetSpinlock tries to occupy a spin-lock variable. If the function returns, either the lock is successfully taken or an error has occurred.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
SpinlockId |
The spin lock number user want to get |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_ID: |
Invalid ID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_INTERFERENCE_DEADLOCK |
Conflict deadlock, lock is already occupied by task |
E_OS_NESTING_DEADLOCK |
Nested deadlock, another task on the same core is occupying another spinlock |
Example
Spinlock_0:LockMethod:LOCK_NOTHING
AccessingApplication: App0,App1
App0: Core: 0
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
App1: Core:1
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL
AccessingApplication:App0
TASK(TaskInit) /* core 0*/
{
GetSpinlock(Spinlock_0);
ActivateTask(Task0);
/*user code*/
ReleaseSpinlock(Spinlock_0);
......
}
TASK(Task0) /* core 1*/
{
GetSpinlock(Spinlock_0);
/*Waiting releasing spinlock on core0*/
/*user code*/
ReleaseSpinlock(Spinlock_0);
......
}
Note
自旋锁机制是一种主动轮询机制。该功能不会引起调度问题。
The spinlock mechanism is an active polling mechanism. This functionality does not cause scheduling issues.
ReleaseSpinlock¶
StatusType ReleaseSpinlock(SpinlockIdType SpinlockId)
ReleaseSpinlock is the counterpart of GetSpinlock. ReleaseSpinlock releases a spinlock variable that was occupied before.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
SpinlockId |
The spin lock number user want to release |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid ID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_STATE |
Spinlock is not occupied by a task |
E_OS_NOFUNC |
The spin locks are released in the wrong order |
Note
在终止任务之前,必须释放通过GetSpinlock占用的所有自旋锁变量。在调用WaitEvent之前,应释放所有自旋锁。
All spinlock variables acquired via GetSpinlock must be released before terminating a task. All spinlocks should be released before calling WaitEvent.
如果ReleaseSpinlock尝试释放未获得的自旋锁,则会发生错误。
An error occurs if ReleaseSpinlock attempts to release a spinlock that has not been acquired.
TryToGetSpinlock¶
StatusType TryToGetSpinlock(SpinlockIdType SpinlockId, TryToGetSpinlockType *Success)
Try to acquire a spinlock.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
SpinlockId |
The spin lock number user want to get |
[out] |
Success |
Returns whether the specified spin lock is occupied |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No Error |
E_OS_ID |
Invalid ID |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong calling environment |
E_OS_DISABLEDINT |
Unable to call system services because of interrupt disable/suspend |
E_OS_ILLEGAL_ADDRESS |
Parameter address access illegal |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this object |
E_OS_INTERFERENCE_DEADLOCK |
Conflict deadlock, lock is already occupied by task |
E_OS_NESTING_DEADLOCK |
Nested deadlock, another task on the same core is occupying another spinlock |
E_OS_ACCESS |
No access to this spin lock |
Example
Spinlock_0:LockMethod:LOCK_NOTHING
AccessingApplication: App0,App1
App0: Core: 0
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
App1: Core: 1
Task0: Priority:2, Preemptive Policy:FULL
AccessingApplication:App0
TASK(TaskInit) /* core 0*/
{
GetSpinlock(Spinlock_0);
ActivateTask(Task0);
/*user code*/
ReleaseSpinlock(Spinlock_0);
......
}
TASK(Task0) /* core 1*/
{
TryToGetSpinlock (Spinlock_0);
/* TryToGetSpinlock return error directly, if the Spinlock_0 is not released on core0*/
......
}
Note
TryToGetSpinlock具有与GetSpinlock相同的功能,不同之处在于,如果自旋锁已被另一个内核上的任务占用,则该函数将设置输出参数”Success”并返回E_OK。
TryToGetSpinlock provides the same functionality as GetSpinlock, except that if the spinlock is already held by a task on another core, this function sets the output parameter “Success” and returns E_OK.
IOC(Functions)¶
IOC负责Os-Application之间的通信,特别是跨越核心或存储器保护边界的通信。 其内部功能与操作系统密切相关。IOC 支持 1:1、N:1 和 N:M 通信。同时支持队列和非队列通信。
The IOC is responsible for communication between OS-Applications, particularly across core or memory protection boundaries. Its internal functionality is closely tied to the operating system. The IOC supports 1:1, N:1, and N:M communication, as well as both queued and non-queued communication.
IocSend_<IocId>[_<SenderId>]¶
StatusType IocSend_<IocId>[_<SenderId>] (<Data> IN, [uint16 numberOfBytesIN])
Send data to implement 1:1 or N:1 queue communication between Os-Applications located on the same or different cores.
- Sync/Async
FALSE
- Reentrancy
This function is generated individually for each sender. A single function is not reentrant (if called from different runnable entities belonging to the same sender), but different functions can be called in parallel.
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
IN |
The data value sent is identified by <IocId>. Parameters are passed by value for primitive data elements and by reference for all other types. |
[in] |
numberOfBytesIN |
Number of bytes to send (optional generation) |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
IOC_E_OK |
The data has been successfully delivered to the communication service. |
IOC_E_LIMIT |
IOC internal communication buffer is full (scenario: receiver is slower than sender). This error will generate an IOC_E_LOST_DATA override error on the receiver side on the next data reception. |
IOC_E_LENGTH |
<numberOfBytesIN> exceeds the internal buffer or is equal to 0, so no data is sent. |
Example
- OsIocBufferLength:20
- OsIocDataProperties:
- OsIocDataProperties_0:
- OsIocDataPropertyIndex:0
- OsIocInitValue:0xFF
- ArrayLength:Not checked
- OsIocDataTypeRef:uint32
- OsIocReceiverProperties:
- OsIocReceiverProperties_0:
- OsIocReceiverId:0
- OsIocReceiverPullCB:ReceiverPullCB_0
- OsIocReceivingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_0_core0
- OsIocSenderProperties:
- OsIocSenderProperties_0:
- OsIocSenderId:0
- OsIocSendingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_1_Core0
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_1*/
{
uint32 Sourcedata = 0xAA;
IocSend_0(Sourcedata);
}
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_0*/
{
uint32 desData;
IocReceive_0(&desData);
}
Note
此接口一般直接由RTE进行调用。
This interface is typically called directly by the RTE.
ORIENTAIS OS支持无RTE时直接调用。
ORIENTAIS OS supports direct invocation without the RTE.
IocWrite_<IocId>[_<SenderId>]¶
StatusType IocWrite_<IocId>[_<SenderId>] (<Data> IN, [uint16 numberOfBytesIN])
Send data to implement 1:1 or N:1 non-queue communication between Os-Applications located on the same or different cores.
- Sync/Async
FALSE
- Reentrancy
This function is generated individually for each sender. A single function is not reentrant (if called from different runnable entities belonging to the same sender), but different functions can be called in parallel.
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
IN |
The data value sent is identified by <IocId>. Parameters are passed by value for primitive data elements and by reference for all other types. |
[in] |
numberOfBytesIN |
Number of bytes to send (optional generation) |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
IOC_E_OK |
The data has been successfully delivered to the communication service. |
Example
- OsIocBufferLength:Not checked
- OsIocDataProperties:
- OsIocDataProperties_0:
- OsIocDataPropertyIndex:0
- OsIocInitValue:0xFF
- ArrayLength:Not checked
- OsIocDataTypeRef:uint32
- OsIocReceiverProperties:
- OsIocReceiverProperties_0:
- OsIocReceiverId:0
- OsIocReceiverPullCB:ReceiverPullCB_0
- OsIocReceivingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_0_core0
- OsIocSenderProperties:
- OsIocSenderProperties_0:
- OsIocSenderId:0
- OsIocSendingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_1_Core0
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_1*/
{
uint32 Sourcedata = 0xAA;
IocWrite_0(Sourcedata);
}
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_0*/
{
uint32 desData;
IocRead_0(&desData);
}
Note
此接口一般直接由RTE进行调用。
This interface is typically called directly by the RTE.
ORIENTAIS OS支持无RTE时直接调用。
ORIENTAIS OS supports direct invocation without the RTE.
IocSendGroup_<IocId>¶
StatusType IocSendGroup_<IocId> (<Data1> IN1, [uint16 numberOfBytesIN1], <Data2> IN2, [uint16 numberOfBytesIN2], ...)
Send a set of data to implement 1:1 or N:1 queue communication between Os-Applications located on the same or different cores.
- Sync/Async
FALSE
- Reentrancy
This function is generated individually for each sender. A single function is not reentrant (if called from different runnable entities belonging to the same sender), but different functions can be called in parallel.
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
IN |
The data value sent is identified by <IocId>. Parameters are passed by value for primitive data elements and by reference for all other types. |
[in] |
numberOfBytesIN |
Number of bytes to send (optional generation) |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
IOC_E_OK |
The data has been successfully delivered to the communication service. |
IOC_E_LIMIT |
The IOC internal communication buffer is full (situation: the receiver is slower than the sender). This error will generate an IOC_E_LOST_DATA override error on the receiver side on the next data reception. |
IOC_E_LENGTH |
<numberOfBytesIN> is outside the internal buffer or equal to 0, so no data will be sent. |
Example
- OsIocBufferLength:20
- OsIocDataProperties:
- OsIocDataProperties_0:
- OsIocDataPropertyIndex:0
- OsIocInitValue:0xFF
- ArrayLength:Not checked
- OsIocDataTypeRef:uint32
- OsIocDataProperties_1:
- OsIocDataPropertyIndex:1
- OsIocInitValue:Not checked
- ArrayLength:20
- OsIocDataTypeRef:uint16
- OsIocReceiverProperties:
- OsIocReceiverProperties_0:
- OsIocReceiverId:0
- OsIocReceiverPullCB:ReceiverPullCB_0
- OsIocReceivingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_0_core0
- OsIocSenderProperties:
- OsIocSenderProperties_0:
- OsIocSenderId:0
- OsIocSendingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_1_Core0
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_1*/
{
uint32 Sourcedata0 = 0xAA;
uint16 Sourcedata1 = 0xAA;
IocSendGroup_0(Sourcedata0 ,Sourcedata1);
}
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_0*/
{
uint32 desData0;
uint32 desData1;
IocReceiveGroup_0(&desData0 ,desData1);
}
Note
此接口一般直接由RTE进行调用。
This interface is typically called directly by the RTE.
ORIENTAIS OS支持无RTE时直接调用。
ORIENTAIS OS supports direct invocation without the RTE.
IocWriteGroup_<IocId>¶
StatusType IocWriteGroup_<IocId> (<Data1> IN1, [uint16 numberOfBytesIN1], <Data2> IN2, [uint16 numberOfBytesIN2], ...)
Send a set of data to achieve 1:1 or N:1 non-queue communication between Os-Applications located on the same or different cores.
- Sync/Async
FALSE
- Reentrancy
This function is generated individually for each sender. A single function is not reentrant (if called from different runnable entities belonging to the same sender), but different functions can be called in parallel.
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
IN |
The data value sent is identified by <IocId>. Parameters are passed by value for primitive data elements and by reference for all other types. |
[in] |
numberOfBytesIN |
Number of bytes to send (optional generation) |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
IOC_E_OK |
The data has been successfully delivered to the communication service. |
IOC_E_LIMIT |
The IOC internal communication buffer is full (situation: the receiver is slower than the sender). This error will generate an IOC_E_LOST_DATA override error on the receiver side on the next data reception. |
IOC_E_LENGTH |
<numberOfBytesIN> is outside the internal buffer or equal to 0, so no data will be sent. |
Example
- OsIocBufferLength:Not checked
- OsIocDataProperties:
- OsIocDataProperties_0:
- OsIocDataPropertyIndex:0
- OsIocInitValue:0xFF
- ArrayLength:Not checked
- OsIocDataTypeRef:uint32
- OsIocDataProperties_1:
- OsIocDataPropertyIndex:1
- OsIocInitValue:Not checked
- ArrayLength:20
- OsIocDataTypeRef:uint16
- OsIocReceiverProperties:
- OsIocReceiverProperties_0:
- OsIocReceiverId:0
- OsIocReceiverPullCB:ReceiverPullCB_0
- OsIocReceivingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_0_core0
- OsIocSenderProperties:
- OsIocSenderProperties_0:
- OsIocSenderId:0
- OsIocSendingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_1_Core0
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_1*/
{
uint32 Sourcedata0 = 0xAA;
uint16 Sourcedata1 = 0xAA;
IocWriteGroup_0(Sourcedata0 ,Sourcedata1);
}
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_0*/
{
uint32 desData0;
uint32 desData1;
IocReadGroup_0(&desData0 ,desData1);
}
Note
此接口一般直接由RTE进行调用。
This interface is typically called directly by the RTE.
ORIENTAIS OS支持无RTE时直接调用。
ORIENTAIS OS supports direct invocation without the RTE.
IocReceive_<IocId>¶
StatusType IocReceive_<IocId> (<Data> OUT, [uint16* numberOfBytesOUT])
Receive data and implement 1:1 or N:1 queue communication between Os-Applications located on the same or different cores.
- Sync/Async
FALSE
- Reentrancy
The function is generated individually for each receiver. A single function is not reentrant (if called from different runnable entities belonging to the same receiver), but different functions can be called in parallel.
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[out] |
OUT |
Receives a data reference for a data element. |
[out] |
numberOfBytesOUT |
Number of bytes to receive (optional generation) |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
IOC_E_OK |
Data was received successfully. |
IOC_E_NO_DATA |
No data is available for reception. |
IOC_E_LOST_DATA |
This Overlayed Error indicates that the IOC communication service refused an IOCSend request from sender due to an internal buffer overflow. There is no error in the data returned in parameter. |
Example
- OsIocBufferLength:20
- OsIocDataProperties:
- OsIocDataProperties_0:
- OsIocDataPropertyIndex:0
- OsIocInitValue:0xFF
- ArrayLength:Not checked
- OsIocDataTypeRef:uint32
- OsIocReceiverProperties:
- OsIocReceiverProperties_0:
- OsIocReceiverId:0
- OsIocReceiverPullCB:ReceiverPullCB_0
- OsIocReceivingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_0_core0
- OsIocSenderProperties:
- OsIocSenderProperties_0:
- OsIocSenderId:0
- OsIocSendingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_1_Core0
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_1*/
{
uint32 Sourcedata = 0xAA;
IocSend_0(Sourcedata);
}
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_0*/
{
uint32 desData;
IocReceive_0(&desData);
}
Note
此接口一般直接由RTE进行调用。
This interface is typically called directly by the RTE.
ORIENTAIS OS支持无RTE时直接调用。
ORIENTAIS OS supports direct invocation without the RTE.
IocRead_<IocId>[_<ReceiverId>]¶
StatusType IocRead_<IocId>[_<ReceiverId>] (<Data> OUT, [uint16* numberOfBytesOUT])
Receive data to implement 1:1 or N:1 non-queue communication between Os-Applications located on the same or different cores.
- Sync/Async
FALSE
- Reentrancy
The function is generated individually for each receiver. A single function is not reentrant (if called from different runnable entities belonging to the same receiver), but different functions can be called in parallel.
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[out] |
OUT |
Receives a data reference for a data element. |
[out] |
numberOfBytesOUT |
Number of bytes to receive (optional generation) |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
IOC_E_OK |
Data was received successfully. |
Example
- OsIocBufferLength:Not checked
- OsIocDataProperties:
- OsIocDataProperties_0:
- OsIocDataPropertyIndex:0
- OsIocInitValue:0xFF
- ArrayLength:Not checked
- OsIocDataTypeRef:uint32
- OsIocReceiverProperties:
- OsIocReceiverProperties_0:
- OsIocReceiverId:0
- OsIocReceiverPullCB:ReceiverPullCB_0
- OsIocReceivingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_0_core0
- OsIocSenderProperties:
- OsIocSenderProperties_0:
- OsIocSenderId:0
- OsIocSendingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_1_Core0
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_1*/
{
uint32 Sourcedata = 0xAA;
IocWrite_0(Sourcedata);
}
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_0*/
{
uint32 desData;
IocRead_0(&desData);
}
Note
此接口一般直接由RTE进行调用。
This interface is typically called directly by the RTE.
ORIENTAIS OS支持无RTE时直接调用。
ORIENTAIS OS supports direct invocation without the RTE.
IocReceiveGroup_<IocId>¶
StatusType IocReceiveGroup_<IocId> (<Data1> OUT1, [uint16* numberOfBytesOUT1], <Data2> OUT2, [uint16* numberOfBytesOUT2], ...)
Receive a set of data to implement 1:1 or N:1 queue communication between Os-Applications located on the same or different cores.
- Sync/Async
FALSE
- Reentrancy
The function is generated individually for each receiver. A single function is not reentrant (if called from different runnable entities belonging to the same receiver), but different functions can be called in parallel.
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[out] |
OUT |
Receives a data reference for a data element. |
[out] |
numberOfBytesOUT |
Number of bytes to receive (optional generation) |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
IOC_E_OK |
Data was received successfully. |
IOC_E_NO_DATA |
No data is available for reception. |
IOC_E_LOST_DATA |
This Overlayed Error indicates that the IOC communication service refused an IOCSend request from sender due to an internal buffer overflow. There is no error in the data returned in parameter. |
Example
- OsIocBufferLength:20
- OsIocDataProperties:
- OsIocDataProperties_0:
- OsIocDataPropertyIndex:0
- OsIocInitValue:0xFF
- ArrayLength:Not checked
- OsIocDataTypeRef:uint32
- OsIocDataProperties_1:
- OsIocDataPropertyIndex:1
- OsIocInitValue:Not checked
- ArrayLength:20
- OsIocDataTypeRef:uint16
- OsIocReceiverProperties:
- OsIocReceiverProperties_0:
- OsIocReceiverId:0
- OsIocReceiverPullCB:ReceiverPullCB_0
- OsIocReceivingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_0_core0
- OsIocSenderProperties:
- OsIocSenderProperties_0:
- OsIocSenderId:0
- OsIocSendingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_1_Core0
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_1*/
{
uint32 Sourcedata0 = 0xAA;
uint16 Sourcedata1 = 0xAA;
IocSendGroup_0(Sourcedata0 ,Sourcedata1);
}
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_0*/
{
uint32 desData0;
uint32 desData1;
IocReceiveGroup_0(&desData0 ,desData1);
}
Note
此接口一般直接由RTE进行调用。
This interface is typically called directly by the RTE.
ORIENTAIS OS支持无RTE时直接调用。
ORIENTAIS OS supports direct invocation without the RTE.
IocReadGroup_<IocId>¶
StatusType IocReadGroup_<IocId> (<Data1> OUT1, [uint16* numberOfBytesOUT1], <Data2> OUT2, [uint16* numberOfBytesOUT2], ...)
Receives a set of data to implement 1:1 or N:1 non-queue communication between Os-Applications located on the same or different cores.
- Sync/Async
FALSE
- Reentrancy
The function is generated individually for each receiver. A single function is not reentrant (if called from different runnable entities belonging to the same receiver), but different functions can be called in parallel.
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[out] |
OUT |
Receives a data reference for a data element. |
[out] |
numberOfBytesOUT |
Number of bytes to receive (optional generation) |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
IOC_E_OK |
Data was received successfully. |
Example
- OsIocBufferLength:Not checked
- OsIocDataProperties:
- OsIocDataProperties_0:
- OsIocDataPropertyIndex:0
- OsIocInitValue:0xFF
- ArrayLength:Not checked
- OsIocDataTypeRef:uint32
- OsIocDataProperties_1:
- OsIocDataPropertyIndex:1
- OsIocInitValue:Not checked
- ArrayLength:20
- OsIocDataTypeRef:uint16
- OsIocReceiverProperties:
- OsIocReceiverProperties_0:
- OsIocReceiverId:0
- OsIocReceiverPullCB:ReceiverPullCB_0
- OsIocReceivingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_0_core0
- OsIocSenderProperties:
- OsIocSenderProperties_0:
- OsIocSenderId:0
- OsIocSendingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_1_Core0
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_1*/
{
uint32 Sourcedata0 = 0xAA;
uint16 Sourcedata1 = 0xAA;
IocWriteGroup_0(Sourcedata0 ,Sourcedata1);
}
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_0*/
{
uint32 desData0;
uint32 desData1;
IocReadGroup_0(&desData0 ,desData1);
}
Note
此接口一般直接由RTE进行调用。
This interface is typically called directly by the RTE.
ORIENTAIS OS支持无RTE时直接调用。
ORIENTAIS OS supports direct invocation without the RTE.
IocEmptyQueue_<IocId>¶
StatusType IocEmptyQueue_<IocId> (void)
If the <IocId> in the function name identifies queued communication, this interface can be called to delete the contents of the IOC internal communication queue.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
IOC_E_OK |
The queue contents were successfully deleted. |
Example
- OsIocBufferLength:20
- OsIocDataProperties:
- OsIocDataProperties_0:
- OsIocDataPropertyIndex:0
- OsIocInitValue:0xFF
- ArrayLength:Not checked
- OsIocDataTypeRef:uint32
- OsIocReceiverProperties:
- OsIocReceiverProperties_0:
- OsIocReceiverId:0
- OsIocReceiverPullCB:ReceiverPullCB_0
- OsIocReceivingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_0_core0
- OsIocSenderProperties:
- OsIocSenderProperties_0:
- OsIocSenderId:0
- OsIocSendingOsApplicationRef:OsApplication_1_Core0
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_1*/
{
uint32 Sourcedata = 0xAA;
IocSend_0(Sourcedata);
IocEmptyQueue_0();
}
TASK(Task0) /* core 0*/ /*OsApplication_0*/
{
uint32 desData;
IocReceive_0(&desData);
}
Note
此接口一般直接由RTE进行调用。
This interface is typically called directly by the RTE.
ORIENTAIS OS支持无RTE时直接调用。
ORIENTAIS OS supports direct invocation without the RTE.
Peripheral(Functions)¶
在某些MCU架构中,存在内存映射的硬件寄存器(外设区域),这些寄存器只能在特定模式(例如特权模式)下访问。只要任务/中断服务例程(Tasks/ISRs)具有完全的硬件访问权限,它们就可以直接访问这些寄存器。如果操作系统使用了内存保护,那么非受信任的操作系统应用程序的任务/中断服务例程不能直接访问这些寄存器,因为这会被操作系统识别为内存违规。
In some MCU architectures, memory-mapped hardware registers (peripheral areas) exist that are accessible only in specific modes (e.g., privileged mode). As long as tasks/interrupt service routines (Tasks/ISRs) have full hardware access rights, they can directly access these registers. If the operating system employs memory protection, tasks/ISRs of untrusted OS-Applications cannot access these registers directly, as this is recognized by the OS as a memory violation.
外设访问的接口被划分为8位、16位和32位。为了简化表达,ReadPeripheral<x>代表ReadPeripheral8、ReadPeripheral16、ReadPeripheral32。WritePeripheral<x>代表WritePeripheral8、WritePeripheral16、WritePeripheral32。ModifyPeripheral<x>代表ModifyPeripheral8、ModifyPeripheral16、ModifyPeripheral32。
Peripheral access interfaces are categorized into 8-bit, 16-bit, and 32-bit types. For simplicity, ReadPeripheral<x> denotes ReadPeripheral8, ReadPeripheral16, and ReadPeripheral32; WritePeripheral<x> denotes WritePeripheral8, WritePeripheral16, and WritePeripheral32; and ModifyPeripheral<x> denotes ModifyPeripheral8, ModifyPeripheral16, and ModifyPeripheral32.
ReadPeripheral<x>¶
StatusType ReadPeripheral8(AreaIdType Area, const uint8 *Address, uint8 *ReadValue)
StatusType ReadPeripheral16(AreaIdType Area, const uint16 *Address, uint16 *ReadValue)
StatusType ReadPeripheral32(AreaIdType Area, const uint32 *Address, uint32 *ReadValue)
This service returns the content of a given memory location (<Address>).
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Area |
hardware peripheral area reference |
[in] |
Address |
memory address, which will be read |
[out] |
ReadValue |
Returned value |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No error |
E_OS_ID |
Area id is out of range (EXTENDED status) |
E_OS_VALUE |
Address does not belong to given Area (EXTENDED status) |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong call context of the API function (EXTENDED status) |
E_OS_ACCESS |
The calling task or ISR is not allowed to access the given |
WritePeripheral<x>¶
StatusType WritePeripheral8(AreaIdType Area, uint8 *Address, uint8 WriteValue)
StatusType WritePeripheral16(AreaIdType Area, uint16 *Address, uint16 WriteValue)
StatusType WritePeripheral32(AreaIdType Area, uint32 *Address, uint32 WriteValue)
This service writes theto a given memory location (<memory address>).
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Area |
hardware peripheral area reference |
[in] |
Address |
memory address, which will be writed |
[in] |
WriteValue |
write value |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No error |
E_OS_ID |
Area id is out of range (EXTENDED status) |
E_OS_VALUE |
Address does not belong to given Area (EXTENDED status) |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong call context of the API function (EXTENDED status) |
E_OS_ACCESS |
The calling task or ISR is not allowed to access the given |
ModifyPeripheral<x>¶
StatusType ModifyPeripheral8(AreaIdType Area, uint8 *Address, uint8 Clearmask, uint8 Setmask)
StatusType ModifyPeripheral16(AreaIdType Area, uint16 *Address, uint16 Clearmask, uint16 Setmask)
StatusType ModifyPeripheral32(AreaIdType Area, uint32 *Address, uint32 Clearmask, uint32 Setmask)
This service modifies a given memory location (<memory address>) with the formula: *<Address> = ((*<Address> & <clearmask>) | <setmask>)
This service modifies a given memory location (<memory address>).
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Area |
hardware peripheral area reference |
[in] |
Address |
memory address, which will be modified |
[in] |
Clearmask |
memory address will be modified by a bit-AND |
[in] |
Setmask |
memory address will be modified by a bit-OR |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
E_OK |
No error |
E_OS_ID |
Area id is out of range (EXTENDED status) |
E_OS_VALUE |
Address does not belong to given Area (EXTENDED status) |
E_OS_CALLEVEL |
Wrong call context of the API function (EXTENDED status) |
E_OS_ACCESS |
The calling task or ISR is not allowed to access the given |
Example
Spinlock_0:LockMethod:LOCK_NOTHING
AccessingApplication: App0,App1
App0: Core: 0
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
TASK(Task0) /* core 1*/
{
uint8* Address8 = REG_XXX1;
uint8 ReadValue8 = 0;
uint16* Address16 = REG_XXX2;
uint16 ModifyValue16 = 165;
uint32* Address32 = REG_XXX3;
StatusType status;
status = ReadPeripheral8 (OsPeripheral_0, Address8, &ReadValue8);
......
status = WritePeripheral16 (OsPeripheral_0, Address16, ModifyValue16);
......
status = ModifyPeripheral32 (OsPeripheral_0, Address32, 0xff, 0xab);
......
}
Extend(Functions)¶
Extend模块为用户提供了一些扩展功能:获取系统堆栈、任务堆栈、ISR堆栈使用情况的接口,检查版本信息的接口,获取检查ISR中断源的接口,检查CPU信息的接口。
The Extend module provides users with several extended functions: interfaces for obtaining system stack, task stack, and ISR stack usage; interfaces for checking version information; interfaces for acquiring and checking ISR interrupt sources; and interfaces for checking CPU information.
OSGetVersionInfo¶
void OSGetVersionInfo(Std_VersionInfoType *osVerInfoPtr)
Provide Version information to user.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[out] |
osVerInfoPtr |
pointer for getting OS version |
- Return type
void
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
TASK(TaskInit)
{
……
Std_VersionInfoType * osVerInfoPtr;
OSGetVersionInfo(osVerInfoPtr);
……
}
OSGetStackUsage¶
osStackUsageType OSGetStackUsage(osStackObject stack, uint16 id)
Get max usage of system,task,ISR2 stack.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
stack |
Stack type |
[in] |
id |
Object ID |
- Return type
osStackUsageType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
uint32 |
Max usage of stack |
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
TASK(TaskInit)
{
……
osStackUsageType MaxUsage;
MaxUsage = OSGetStackUsage(OS_STACK_TASK, TaskInit);
……
}
OSCheckISRSource¶
StatusType OSCheckISRSource(uint32 Source)
OSCheckISRSource is used to check the interrupt source.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
Parameters
Dir |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
[in] |
Source |
Isr source |
- Return type
StatusType
Return values
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
TRUE |
current triggered interrupt. |
FALSE |
not current triggered interrupt. |
Example
/*
*ISR(ISR_DMA_SF_DMA0_CH_0: Core0(CPU0))
*/
ISR(ISR_DMA_SF_DMA0_CH_0)
{
……
StatusType ret;
ret = OSCheckISRSource(DMA_SF_DMA0_CH_0)
……
}
OSCheckCPUInformation¶
void OSCheckCPUInformation(void)
OSCheckCPUInformation is used to check if the CPU information is correct.
- Sync/Async
TRUE
- Reentrancy
Non Reentrant
- Return type
void
Example
TaskInit: Priority:1, Preemptive Policy:FULL, Autostart:True
void main()
{
......
OSCheckCPUInformation();
StartOS(OSDEFAULTAPPMODE);
......
}
配置(Configuration)¶
本章主要介绍OS模块的配置参数。它主要包括配置界面上显示的名称,相应的标准,值范围,默认值,参数说明和相关性。它旨在帮助用户使用配置工具来完成OS模块的配置。
This chapter describes the configuration parameters of the OS module. It covers the names displayed on the configuration interface, corresponding standards, value ranges, default values, parameter descriptions, and dependencies. It aims to assist users in completing OS module configuration using the configuration tool.
OS基本对象配置(OS Basic Object Configuration)¶
控制系统运行的关键数据可以抽象为一系列的OS对象,以下简单说明OS运行过程中所必须配置的一些关键实体:
The key data controlling system operation can be abstracted into a series of OS objects. The following briefly describes key entities that must be configured during OS operation:
OS对象(OS Object)¶
OS基本配置如下:
The basic OS configurations are as follows:
OS对象配置(OS Object Configuration)¶
Core运行数量、Scalability Class(OS运行可拓展等级)、OsHooks等关键配置由此页面配置。
Key configurations such as the number of running cores, Scalability Class (OS scalability level), and OsHooks are configured on this page.
SystemTimer对象(SystemTimer Object)¶
SystemTimer对象主要用于生成OS正常运行依赖的一系列中断:如时钟中断、时间保护中断、跨核通信中断(多核使用)。
The SystemTimer object is primarily used to generate a series of interrupts required for normal OS operation, such as clock interrupts, time protection interrupts, and cross-core communication interrupts (for multi-core systems).
SystemTimer对象配置(SystemTimer Object Configuration)¶
Note
用户配置SystemTimer对象默认生成OS所依赖的中断,建议如非必要请不要修改此类中断频率,优先级等配置数据。
The interrupts required by the OS are generated by default when configuring the SystemTimer object. It is recommended not to modify configuration data such as interrupt frequency and priority unless necessary.
Counter对象(Counter Object)¶
Counter对象主要用于生成OS所依赖的计时器,可分为软件counter与硬件counter两类。
Counter objects are primarily used to generate timers required by the OS, which can be categorized into software counters and hardware counters.
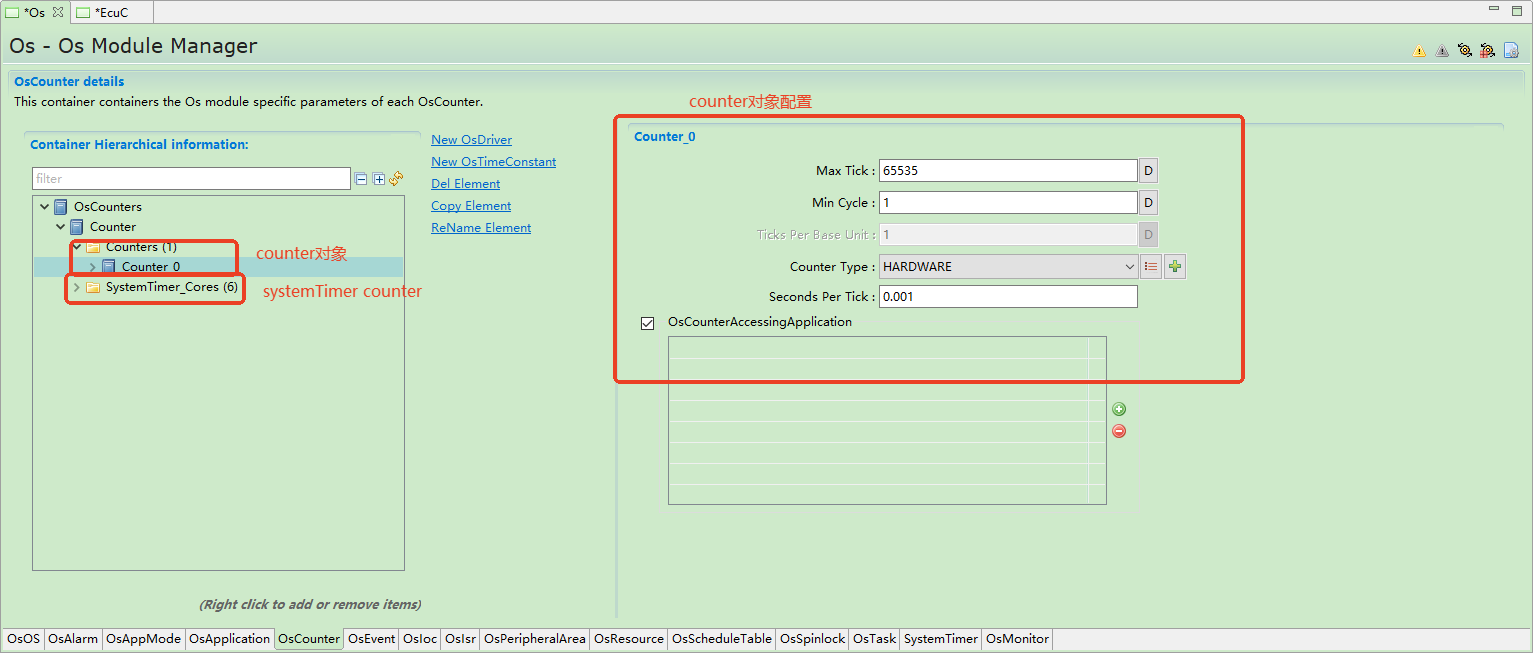
Counter对象配置(Counter Object Configuration)¶
Note
用户配置Counter对象后将默认生成SystemTimer所关联的Counter。
Configuring a Counter object will generate the Counter associated with the SystemTimer by default.
Task对象配置(Task Object Configuration)¶
Task对象是用户代码的执行者,配置该对象将在Os_UserInf.c中生成任务对应的entry,用户可以在entry中添加自己的代码或调用AUTOSAR规范定义的标准API以实现自己的功能需求。
The Task object executes user code. Configuring this object generates the corresponding task entry in Os_UserInf.c. Users can add their code to the entry or call standard APIs defined by the AUTOSAR specification to implement their functional requirements.
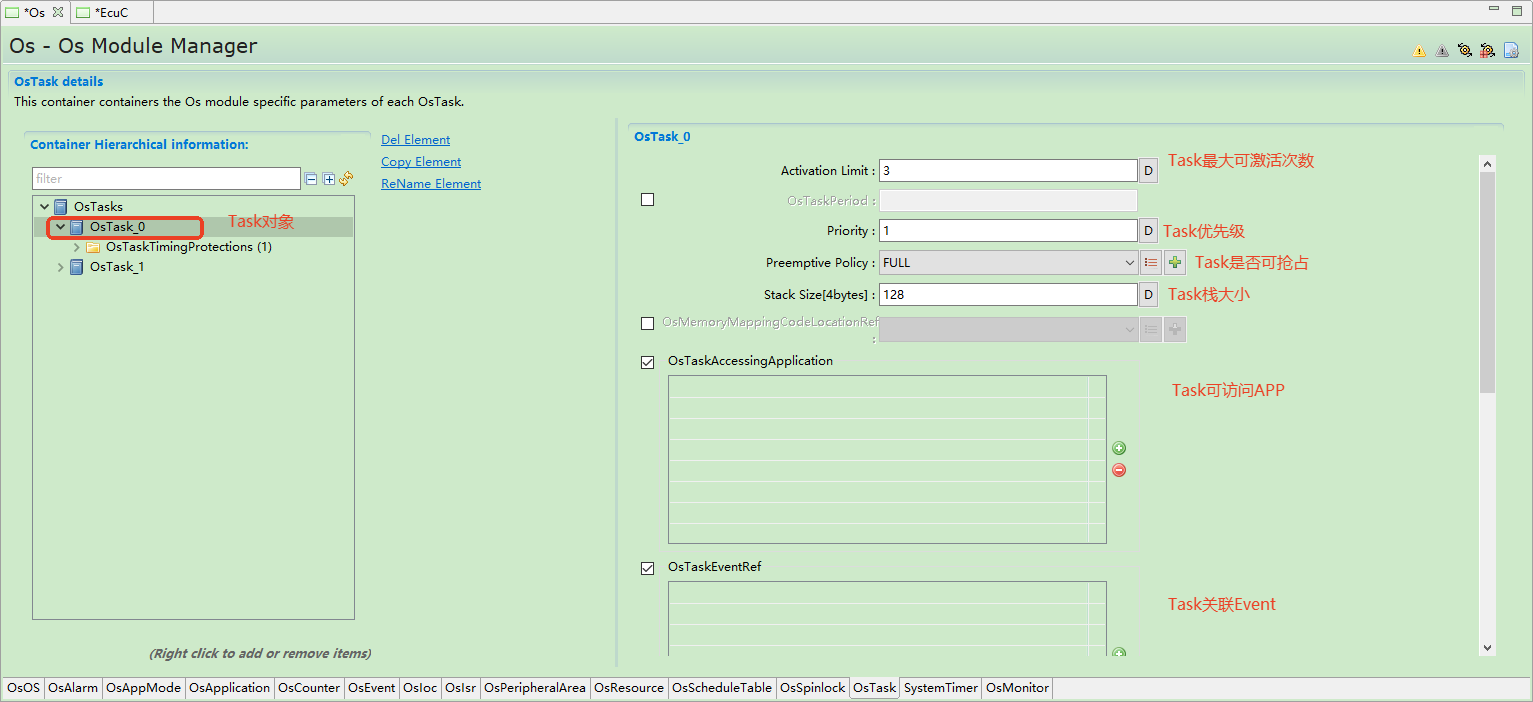
Task对象配置(Task Object Configuration)¶
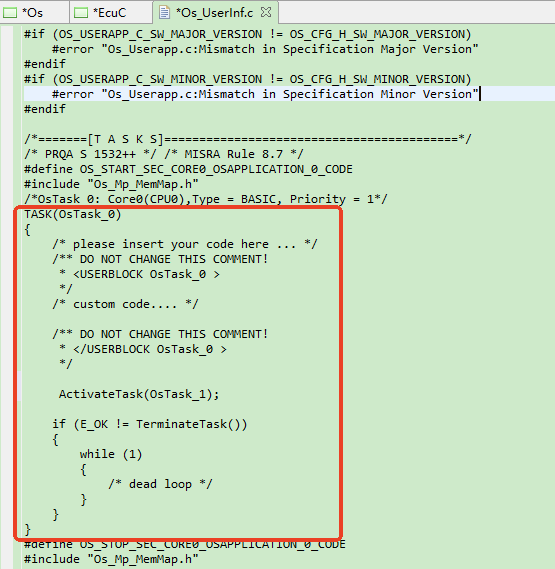
Task entry¶
Note
用户还可在Task对象中关联所需的Event、Resource从而实现任务的同步和对关键资源的访问。
Users can also associate required Events and Resources with the Task object to achieve task synchronization and access to critical resources.
ISR对象配置(ISR Object Configuration)¶
ISR对象是中断执行的载体,分为二类中断与一类中断两类。二类中断受OS的管理控制且可以调用AUTOSAR规范定义的标准API,一类中断则不受OS控制可能会引起一些未定义的行为。
The ISR object serves as the carrier for interrupt execution, divided into Category 2 interrupts and Category 1 interrupts. Category 2 interrupts are managed by the OS and can call standard APIs defined by the AUTOSAR specification, while Category 1 interrupts are not OS-controlled and may cause undefined behavior.
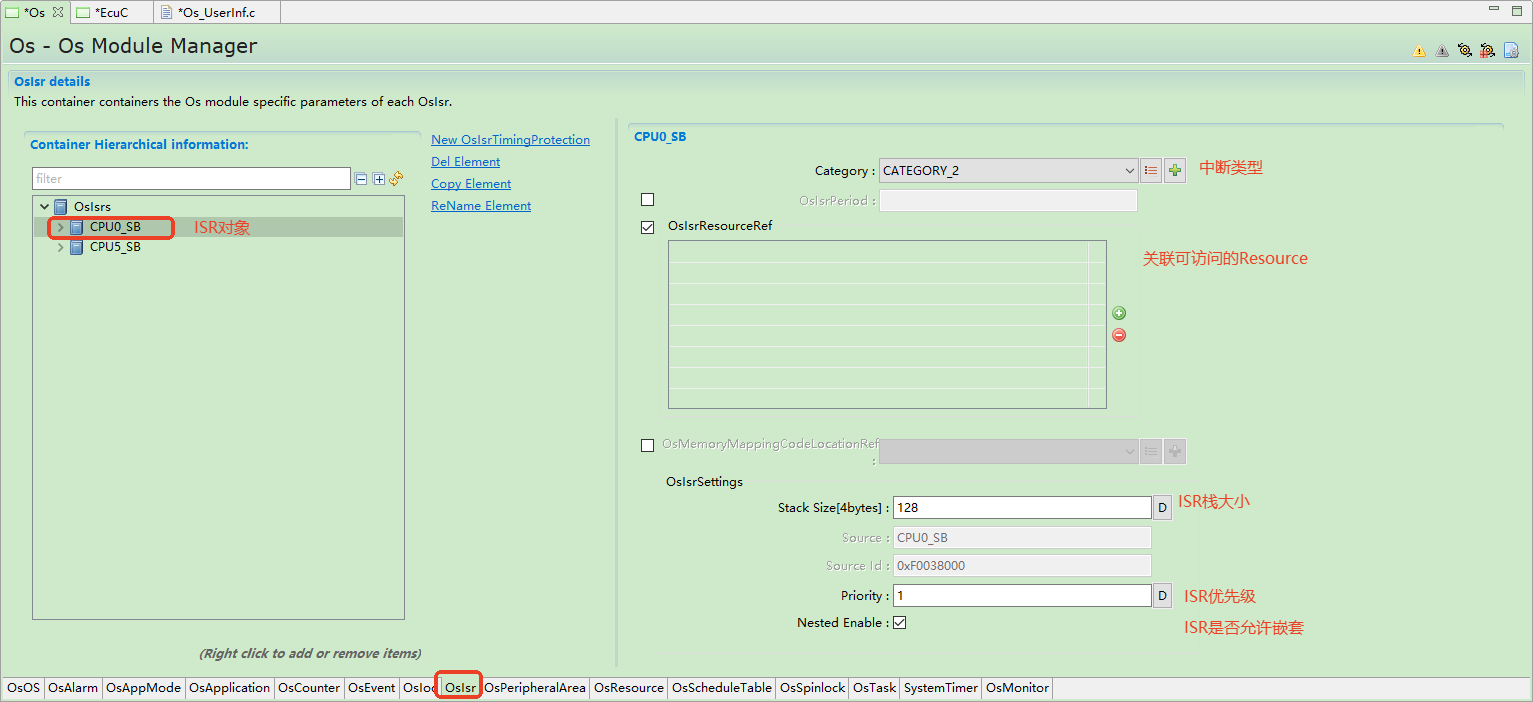
ISR对象配置(ISR Object Configuration)¶
Alarm对象配置(Alarm Object Configuration)¶
Alarm对象主要用于在设置的counter计数点执行对应的动作。如激活任务、调用用户回调函数、增加counter计数、设置Event。使用Alarm必须关联对应的counter作为触发者。
The Alarm object is primarily used to execute corresponding actions at configured counter counting points, such as activating tasks, calling user callback functions, incrementing counter counts, and setting Events. Using an Alarm requires association with a corresponding counter as the trigger.
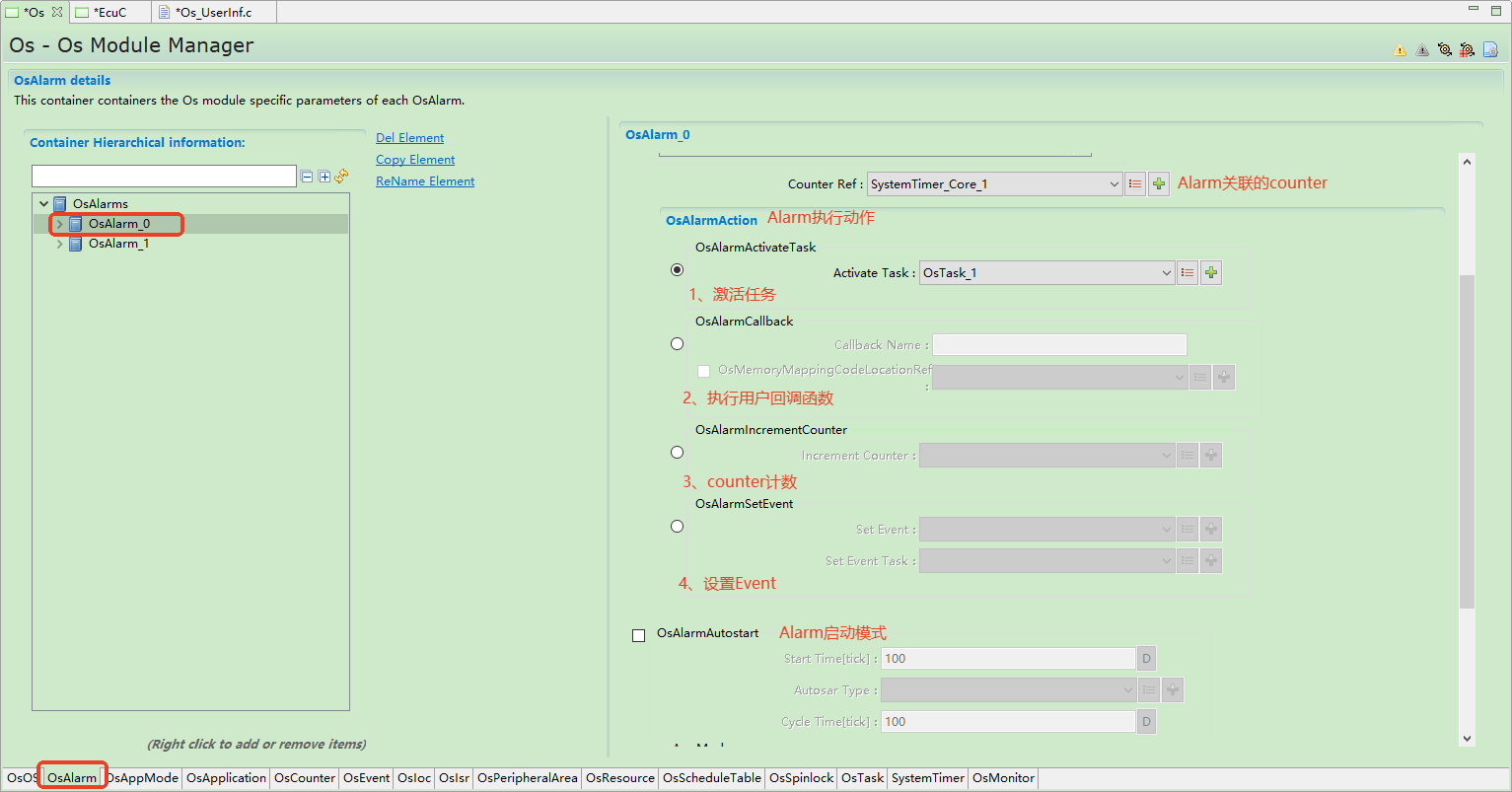
Alarm对象配置(Alarm Object Configuration)¶
APP对象配置(APP Object Configuration)¶
AUTOSAR OS 能够支持构成一个内聚功能单元的操作系统对象集合(任务、ISR、警报、计划表、计数器)。此对象集合称为 OS Application。
AUTOSAR OS supports collections of operating system objects (tasks, ISRs, alarms, schedule tables, counters) that form cohesive functional units. These collections are called OS Applications.
操作系统模块负责在共享处理器的Application之间调度可用的处理资源。如果使用Application,则所有任务、ISR、计数器、警报和计划表都必须属于一个Application。属于同一Application的所有对象都可以相互访问。在配置期间可以授予访问其他Application对象的权限。
The operating system module schedules available processing resources among Applications sharing a processor. When using Applications, all tasks, ISRs, counters, alarms, and schedule tables must belong to an Application. All objects within the same Application can access each other. Permissions to access objects of other Applications can be granted during configuration.
Application可分为:不可信APP、可信不带保护APP、可信带保护APP。配合内存保护功能可以实现不同类型的APP对不同数据段和代码段的控制访问。
Applications are categorized as: untrusted Applications, trusted Applications without protection, and trusted Applications with protection. Combined with memory protection functionality, this enables different Application types to have controlled access to different data and code segments.
App安全机制 App Security Mechanisms
限制非信任OS应用调用服务(非信任OS应用不能调用ShutdownOS和ShutdownAllCores服务),超出限制直接返回。
Untrusted OS Applications are restricted from calling certain services (they cannot call ShutdownOS and ShutdownAllCores services). If restrictions are violated, the call returns immediately.
如果超出配置的权限,操作系统应用程序访问另一个应用程序的对象将触发服务保护错误,返回的错误代码应由用户处理。
Accessing another Application’s objects beyond configured permissions triggers a service protection error. The returned error code should be handled by the user.
如果输入参数无效,则应在 OS 应用程序模块中触发错误挂钩,用户应决定如何处理。
Invalid input parameters trigger an error hook in the OS application module. The user should determine appropriate handling.
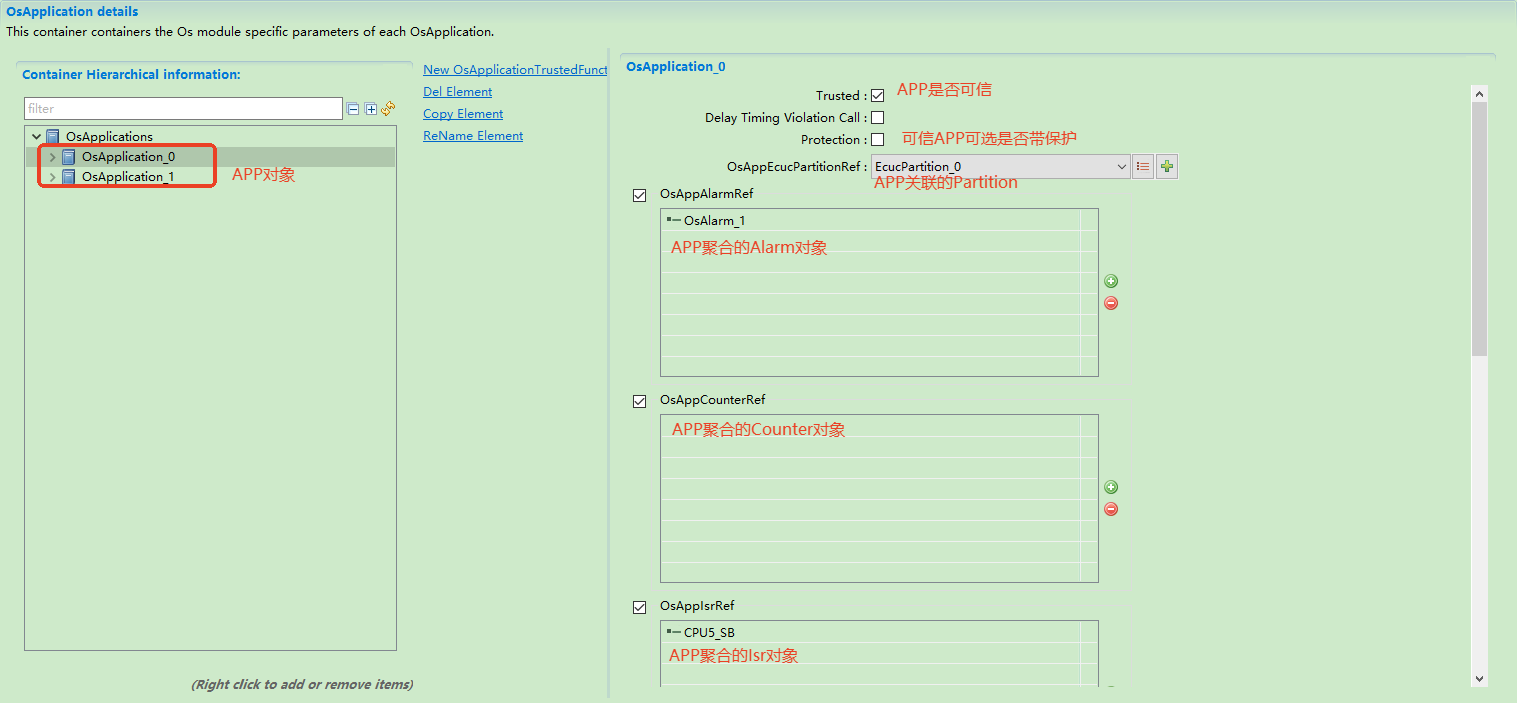
APP对象配置(APP Object Configuration)¶
OS多核配置 OS Multi-Core(Configuration)¶
要配置OS多核,必须在工具中配置EcuC模块,然后再工具OS模块中由Partition关联到不同的核上。
To configure OS multi-core, the EcuC module must be configured in the tool, and then Partitions are associated with different cores in the tool’s OS module.
EcuC配置多核 EcuC Configuration for Multi-Core¶
EcuC首先需要配置Core对象,确定工程中Core的数量及ID。
First, EcuC requires configuration of Core objects to determine the number and IDs of Cores in the project.
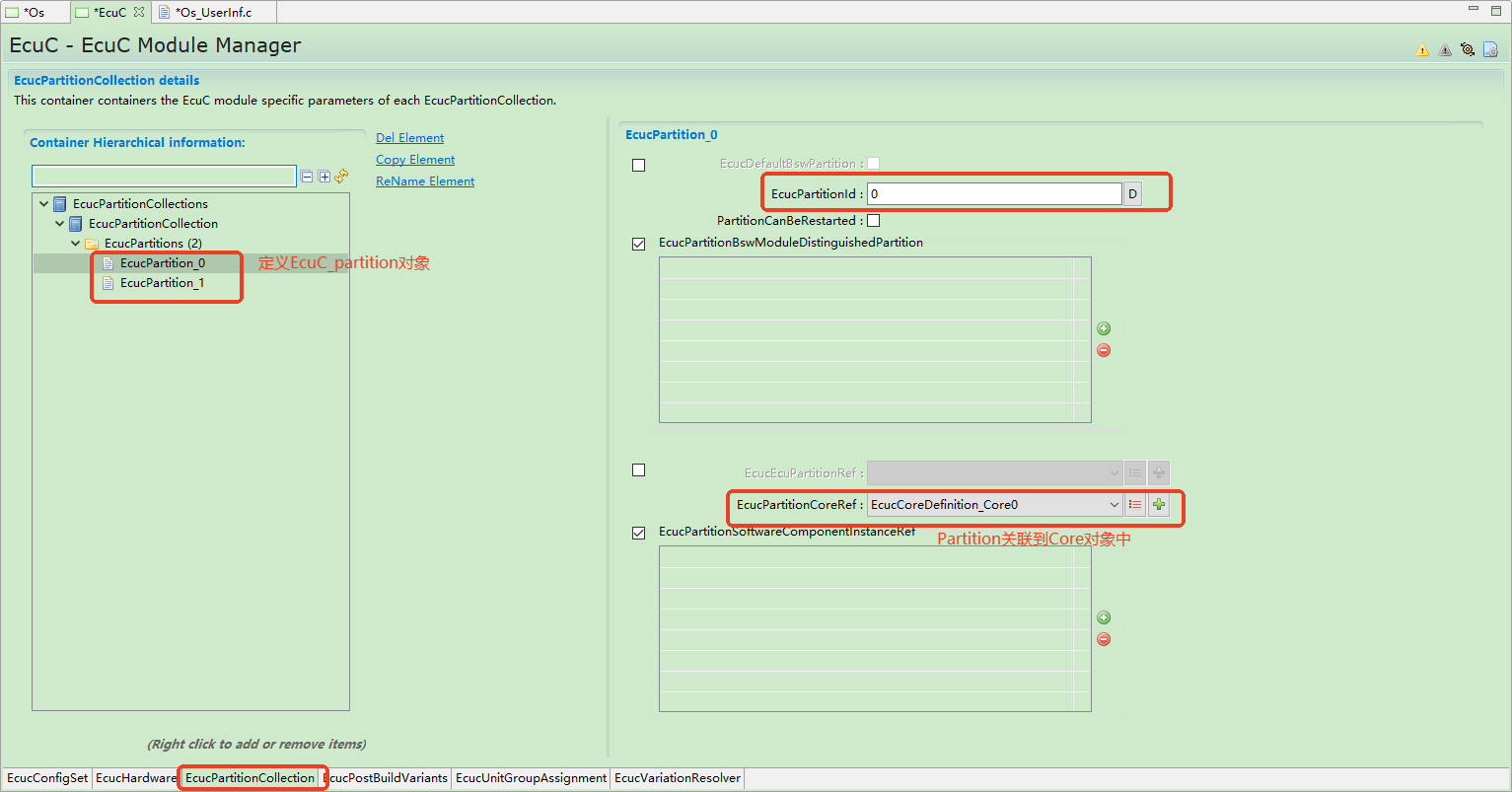
EcuC配置Partition对象(EcuC Partition Object Configuration)¶
之后EcuC定义EcuC Partition对象,并将Partition对象关联到之前配置的Core对象当中。
EcuC then defines EcuC Partition objects and associates these Partition objects with the previously configured Core objects.
OS配置多核 OS Configuring Multi-Core¶
OS首先需要在OSos对象中,配置Core num(必须与EcuC配置的Core对象数量一致)。
First, OS needs to configure Core num in the OSos object (this must match the number of Core objects configured in EcuC).
然后,OS在OSAPP中,关联EcuC Partition对象,从而映射到不同的Core当中。
Then, OS associates EcuC Partition objects in OSAPP to map to different Cores.
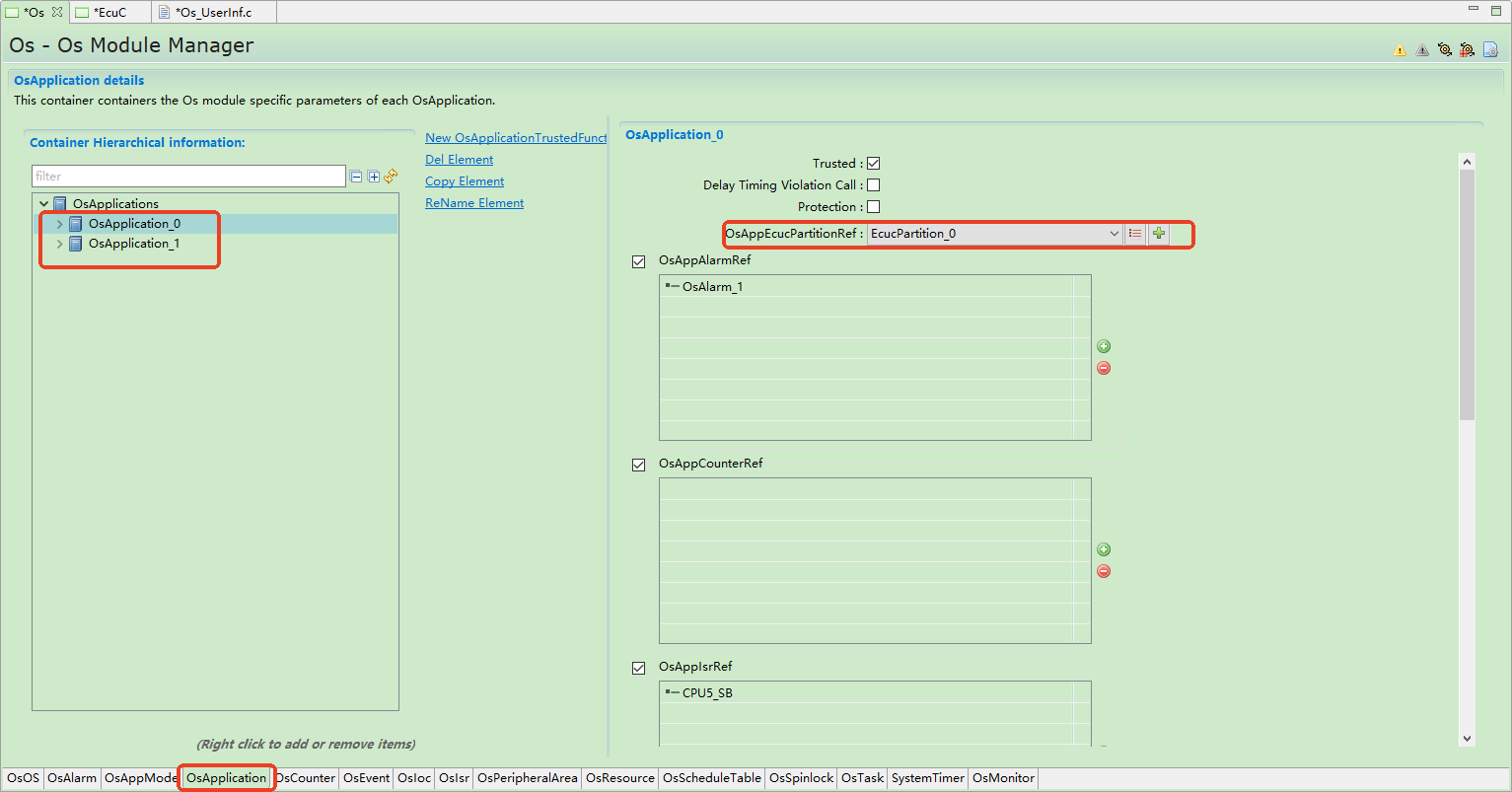
OS配置Partition对象(OS Partition Object Configuration)¶
OS保护功能配置(OS Protection Function Configuration)¶
时间保护(Time Protection)¶
当任务或中断在运行时错过其截止时间时,就会发生实时系统中的计时故障。
Timing failures in real-time systems occur when tasks or interrupts miss their deadlines during operation.
为了安全、准确地保护时间,操作系统必须在运行时控制以下因素,以确保任务/ISR 能够满足各自的截止期限:
For safe and accurate time protection, the operating system must control the following factors at runtime to ensure tasks/ISRs meet their respective deadlines:
系统中Task/ISR的执行时间
Task/ISR execution time in the system
低优先级任务/ISR 锁定共享资源或禁用中断时,任务/ISR 所遭受的阻塞时间
Blocking time experienced by tasks/ISRs when low-priority tasks/ISRs lock shared resources or disable interrupts
系统中Task/ISR的到达间隔率。
Task/ISR arrival interval rate in the system.
AUTOSAR OS 通过使用执行时序保护来保证执行时间的静态配置上限(称为执行预算),从而防止(1)出现时序错误:
AUTOSAR OS prevents timing errors in (1) through execution timing protection, which ensures a statically configured upper limit of execution time (called execution budget) for:
任务(Tasks)
第2类ISR(Category 2 ISRs)
AUTOSAR OS 通过使用锁定时序保护来保证静态配置的上限(称为锁定预算),从而防止出现(2)的时序错误,时间如下:
AUTOSAR OS prevents timing errors in (2) through lock timing protection, which ensures a statically configured upper limit (called lock budget) for:
资源由任务/第2类ISR持有(Resources held by tasks/Category 2 ISRs)
操作系统中断被任务/第2类ISR暂停(OS interrupts disabled by tasks/Category 2 ISRs)
所有中断均被任务/第2类ISR暂停/禁用(All interrupts disabled by tasks/Category 2 ISRs)
AUTOSAR OS 通过使用到达间隔时序保护来保证以下时间的静态配置下限(称为时间帧),从而防止出现(3)中的时序错误:
AUTOSAR OS prevents timing errors in (3) through arrival interval timing protection, which ensures a statically configured lower limit (called time frame) for:
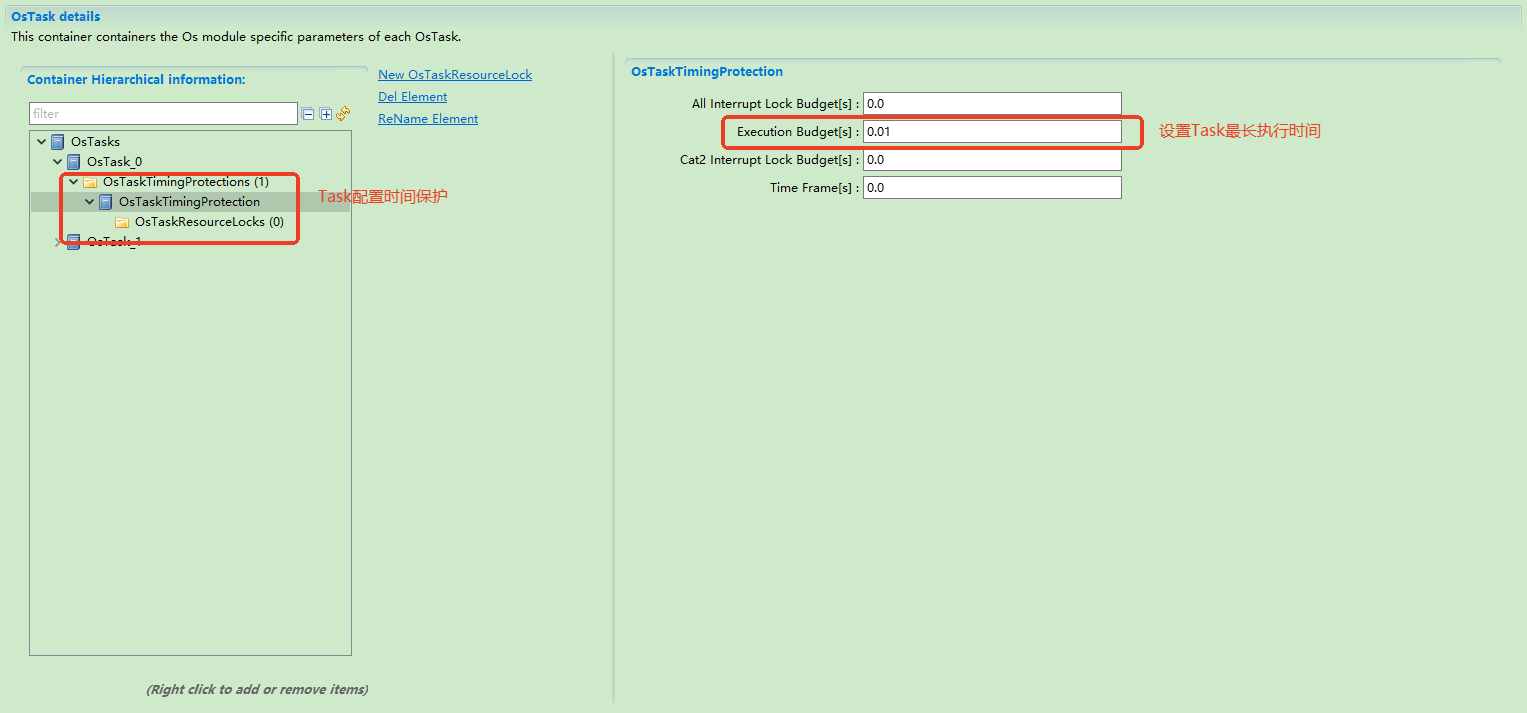
Task配置时间保护功能(Task Time Protection Configuration)¶
Note
该功能依赖于额外的高精度时钟。
This function depends on an additional high-precision clock.
OS在可扩展等级为SC2、SC4时提供该功能。
The OS provides this function at scalability levels SC2 and SC4.
内存保护(Memory Protection)¶
内存保护限制对内存的访问(读/写/执行)。超过限制会触发内存保护异常,然后进入保护钩子,由用户处理。
Memory protection restricts memory access (read/write/execute). Exceeding these restrictions triggers a memory protection exception, which then invokes the protection hook for user handling.
该保护功能通常与APP配合使用,从而限制不可信APP对关键代码和数据的访问。
This protection function is typically used with Applications to restrict untrusted Applications from accessing critical code and data.
Note
内存保护仅在提供内存保护硬件支持的处理器上才可行。内存保护方案基于可执行程序的(数据、代码和堆栈)部分。
Memory protection is only feasible on processors with hardware memory protection support. The memory protection scheme is based on the executable program’s sections (data, code, and stack).
OS在可扩展等级为SC3、SC4时提供该功能。
The OS provides this function at scalability levels SC3 and SC4.
服务保护(Service Protection)¶
由于操作系统应用程序可以通过服务与操作系统模块交互,因此服务调用不会损坏操作系统模块本身至关重要。服务保护在运行时防止此类损坏。
Since OS Applications interact with OS modules through services, it is crucial that service calls do not damage the OS modules themselves. Service protection prevents such damage during runtime.
服务保护有许多情况需要考虑:操作系统应用程序进行API调用
Service protection considers multiple scenarios when an OS Application makes API calls:
句柄无效或值超出范围。
Invalid handle or value out of range.
在错误的上下文中,例如在StartupHook()中调用ActivateTask()。
Incorrect context, such as calling ActivateTask() within StartupHook().
或未能进行API调用,导致ORIENTAIS OS处于未定义状态,例如,它在不调用ReleaseResource()的情况下终止。
Failure to make required API calls, leaving ORIENTAIS OS in an undefined state, such as terminating without calling ReleaseResource().
这会影响系统中其他所有操作系统应用程序的行为,例如ShutdownOS()
Affecting behavior of all other OS Applications in the system, such as calling ShutdownOS()
操纵属于另一个操作系统应用程序(它没有必要的权限)的操作系统对象,例如,操作系统应用程式试图对它不拥有的任务执行ActivateTask()。
Manipulating OS objects belonging to another OS Application without necessary permissions, such as attempting ActivateTask() on a task not owned by the Application.
ORIENTAIS OS已经通过服务调用返回的状态码提供了一些服务保护,这将为服务保护提供基础。这意味着服务保护仅适用于ORIENTAIS OS的扩展状态。
ORIENTAIS OS already provides basic service protection through status codes returned by service calls, which form the foundation for service protection. This means service protection applies only to ORIENTAIS OS extended states.
配置服务保护(Service Protection Configuration)¶